digital
Funding innovation in 2026 is no longer a “local” exercise. For global businesses, the fastest route to better cashflow, reduced risk and accelerated scale is a joined-up strategy that blends grants, tax incentives and country-by-country delivery, without losing control of compliance.
At FI Group by EPSA, we see the same pattern across sectors: where R&D is genuinely global, the funding approach must be global too.
Why a global approach matters in 2026
Innovation funding is expanding in both complexity and scrutiny. Tax authorities want better evidence, funders want clearer impact, and many schemes now include location rules, collaboration requirements and stricter reporting.
In the UK alone, the latest published HMRC statistics show £7.6bn of support claimed under R&D tax credits in 2023 to 2024. That scale explains why governance, documentation and “right first time” submission have become non-negotiable.
Meanwhile, businesses are increasingly expected to “stack” support intelligently, not just chase the biggest headline scheme.
“The finance edge comes from stacking non-dilutive funding from local and international schemes, making innovation risk manageable and more profitable.”
Fawzi Abou-Chahine, Funding Director, FI Group by EPSA UK
That is the mindset behind a global innovation funding operating model.
What is a global innovation funding strategy?
A global innovation funding strategy is a coordinated plan that matches your R&D roadmap to the best available support in each territory, then governs delivery so claims and applications work together rather than collide.
Two core building blocks:
- Grant funding: Competitive, non-dilutive public funding (often with specific themes, deadlines, consortium rules and reporting duties).
- R&D tax relief: A rules-based tax incentive that reduces corporation tax or provides a payable credit based on qualifying R&D expenditure.
The strategic aim is to combine both, where permitted, while managing interactions such as state aid, “double funding” restrictions and differing definitions of eligible costs.
How we build cross-border funding innovation in 2026
FI Group’s approach is deliberately practical: align the funding plan to how the business actually runs, then execute locally with global coordination. Our teams support companies to identify and secure optimal financing conditions for R&D and innovation, from local tax incentives to national and international grants and loans.
1) Map the R&D footprint and funding “right to claim”
We start with a clear view of:
- Where technical work happens (countries, sites, labs, suppliers).
- Who employs the teams and owns the IP.
- Which cost categories sit in which legal entities.
- Which projects are good candidates for grants versus tax incentives.
This matters because many regimes apply overseas restrictions or location tests. For example, the UK’s merged scheme notes restrictions on some overseas expenditure.
2) Define the “global project narrative”, then localise it
Your technical story must be consistent globally, but written to local tests.
A strong model is:
- One master technical narrative (uncertainty, advance, competent professional baseline).
- Local annexes for each country’s definitions, eligible cost rules and record-keeping.
This becomes vital where administrations require extra disclosure. In the UK, HMRC introduced an Additional Information Form requirement for claims from 8 August 2023.
3) Build the funding stack by work package
We split the R&D plan into work packages, then assign the right funding pathway:
- Foundational research and feasibility: grants (where time-to-cash is acceptable).
- Productisation and scale: a mix of grants, loans and tax incentives.
- Manufacturing and industrialisation: location-specific programmes and strategic funds.
This is where funding innovation in 2026 becomes a portfolio discipline, not a one-off application.
4) Execute locally, govern globally
Local execution protects eligibility. Global governance protects consistency.
In practice this means:
- Local specialists handling country rules, language and funder expectations.
- A single global governance layer controlling project boundaries, evidence, cost allocations and interactions between schemes.
This “local delivery, global control” model is central to successful cross-border R&D funding.
Snapshot: grants and R&D tax incentives across key jurisdictions
Below is a practical snapshot of major grant pools and headline R&D tax incentive rates, using the latest publicly available figures as at January 2026. Funding volumes and effective benefit vary by company profile, sector and project design.
UK
Grant landscape, recent indicators
- Innovate UK runs frequent competitions. A single Growth Catalyst round has offered up to £100m in funding.
- UKRI reporting shows that in 2024 to 2025, Innovate UK handled over 17,000 applications requesting £9.6bn in total funding.
R&D tax incentive headline (2026 rules)
- Merged RDEC expenditure credit rate: 20%.
- ERIS for loss-making R&D-intensive SMEs: up to 14.5% payable credit on surrenderable loss, with a 186% total deduction.
Ireland
Grant landscape, latest published programme data
- Enterprise Ireland reports 125 in-company R&D support grants approved in 2024.
- DTIF approvals of €11.4m for two new projects in 2024, with €376m cumulative funding awarded across seven calls.
R&D tax incentive headline (2026 update)
- Budget 2026 measures indicate the Irish R&D tax credit increases from 30% to 35%, with a higher first-year payment threshold of €87,500.
European Union
Grant landscape
- Horizon Europe total budget: €95.5bn (2021–2027).
- EIC Accelerator: grant up to €2.5m, plus equity investment typically €0.5m to €15m.
- STEP Scale-up: investments up to €30m (as described in EIC communications).
Spain
Grant landscape
- CDTI states its 2025 support volume reaches up to €1.942bn across grants, direct expenditure, venture capital investment and loans with a subsidy tranche.
- CDTI’s NEOTEC 2025 call: €40m awarded to 130 innovative SMEs.
R&D tax incentive headline
- Spain’s R&D tax credit design includes a 25% credit on the average of prior spend and 42% on the excess above that average, with an 8% deduction for certain R&D assets, plus refund mechanisms subject to conditions.
Singapore
Grant and public R&D investment landscape
- RIE2025 plan: S$25bn committed to R&D (2021–2025).
- RIE2030 plan: S$37bn announced for the next five years.
R&D tax incentive headline
- Enhanced deduction of 250% of qualifying R&D expenditure for YA 2019 to 2028 (for R&D carried out in Singapore).
- For YA 2024 to 2028, an enhanced 400% deduction applies to the first SGD 400,000 of qualifying R&D spend (with conditions).
United States
Grant landscape
- SBIR in FY2023: over 5,000 awards valued at nearly $4bn (per SBA data cited by GAO).
- SBA’s FY2022 annual report: $4.73bn total obligations across SBIR ($4.12bn) and STTR ($618.3m).
- SBIR/STTR set-asides: 3.2% (SBIR) and 0.45% (STTR).
R&D tax incentive headline
- Federal research credit (IRC §41): 20% of the excess over the base amount (regular method).
- Alternative simplified credit: 14% of qualifying research expenses above 50% of the prior three-year average.
South America example: Brazil
Brazil offers both grant-style support (varying by call and agency) and tax incentives. One widely used incentive is Lei do Bem, which provides an additional deduction of 60% to 100% on eligible R&D spend, equating to a tax reduction of 20.4% to 34%. Activities must be carried out in Brazil.
Mini case study: structuring a US–UK–Spain R&D funding strategy
Scenario (illustrative): A global industrial software company has:
- A core product engineering team in the US (platform and AI).
- A UK team focused on applied R&D and customer-driven prototypes.
- A Spanish team building embedded integrations and validation tooling.
A structured funding plan could look like this:
Define work packages that match each jurisdiction’s strengths
- US: foundational algorithms, cloud architecture, experimental development.
- UK: applied R&D, prototype build, pilot deployments.
- Spain: engineering validation, integration tooling, test rigs.
Align each work package to the right support
- US: SBIR/STTR for early-stage technology risk, plus federal R&D tax credit.
- UK: Innovate UK competitions for collaborative applied R&D, plus merged RDEC or ERIS depending on profile.
- Spain: CDTI programmes for business-led technology projects, plus Spanish R&D tax credits.
Create one evidence pack, three compliant outputs
- One master technical narrative and work package plan.
- Localised claim narratives and cost treatments (UK, US, ES).
- A single global R&D cost tracking approach, so evidence is consistent in audit.
Add a “global bet”
Where the innovation is truly collaborative and scalable, consider an EU route (EIC Accelerator or Horizon Europe consortia), especially where the Spanish entity can lead EU engagement.
Outcome
The strategy improves cash runway, reduces reliance on a single funding source and increases certainty of delivery, because funding is attached to defined work packages rather than vague “innovation spending”.
Common CFO challenges in 2026 and how to mitigate them
- Different definitions of R&D across countries
Mitigation: maintain a master definition, then localise eligibility tests and documentation. - Overseas cost restrictions and subcontracting rules
Mitigation: map supply chains early and confirm location eligibility before committing spend. - Cashflow timing differences (tax credit vs grant reimbursement)
Mitigation: build a funding calendar and use a blended mix to smooth cashflow. - Increased disclosure and audit focus
Mitigation: treat evidence like a product, standard templates, version control, technical sign-off, and consistent cost allocation. - Interaction risk: claiming tax relief on grant-funded costs
Mitigation: ring-fence funded work packages and maintain a clear funding ledger per project.
FI Group by EPSA insight
FI Group by EPSA operates internationally with a dedicated incentives and grants capability, supporting businesses to access funding across geographies and industries. Our international team includes over 1,400 experts across 13 countries, supporting 15,000 clients worldwide and securing over €1.7bn in funding annually, which is why many multinational groups use FI Group to coordinate multi-country innovation funding strategies with consistent governance and local compliance.
Actionable steps for funding innovation in 2026
- Build a 12-month “funding map” by country, entity and project.
- Prioritise 3–5 work packages that can credibly win competitive grants.
- Choose your hubs (UK, Ireland, Spain, Singapore, US) based on where the real technical risk sits.
- Standardise evidence collection (technical baselines, test logs, version history, timesheets).
- Run a quarterly governance review to prevent double-funding and keep submissions aligned.
- Refresh the strategy annually, as rates, thresholds and call themes change.
FAQs
1) Can we combine grants and R&D tax relief on the same project?
Often yes, but you must manage interaction rules, particularly whether the grant is considered state aid or restricts claiming on the same cost base.
2) Which countries are best for innovation hubs in 2026?
It depends on your footprint and sector. The UK, Ireland, Spain, Singapore and the US each offer distinct mixes of grants and tax incentives.
3) What is the biggest failure mode in cross-border funding?
Treating each application or claim as a standalone activity, rather than as part of one governed portfolio.
4) How do we avoid double funding issues?
Separate work packages, track funding sources per cost line, and maintain auditable links between technical deliverables and financial records.
5) What should we do first if we have never built a global funding strategy?
Start with a footprint map and a shortlist of projects, then design a two-track plan: quick wins (tax incentives) and strategic bids (grants).
That mindset is changing rapidly. The average global cost of a data breach reached USD 4.88 million in 2024, marking a significant year‑on‑year increase and highlighting the severe financial and reputational consequences of inadequate protection. But the true cost goes far beyond fines and incident response. Recent research shows that 87% of consumers would not do business with a company if they had concerns about its security practices or recent security and privacy incidents. This convergence of escalating risk and eroding trust demands a fundamental rethink.
The question is no longer:
How can we meet minimum compliance requirements?The strategic imperative today is:
How can we transform investment in robust privacy and cutting‑edge cybersecurity into a measurable competitive advantage that drives sustainable business growth?
At FI Group, we see this as the dawn of the Trust Economy. Compliance is the floor; trust is the ceiling. This article explores why a proactive, globally aware approach to privacy and security—one that goes beyond compliance—is the single most critical investment for securing your future, enhancing market positioning, and unlocking new revenue streams.
From Cost Mitigation to Value Creation
The rise of cyber threats, from ransomware‑as‑a‑service to state‑sponsored espionage, requires a strategic shift. Every amount spent on advanced security and privacy is not a tax on innovation but an investment in resilience and market leadership.
Pillar 1: Cybersecurity as a Strategic Enabler of Global Operational Efficiency
In a hyper‑connected world, business continuity depends on cyber resilience. The ROI of cybersecurity is best measured by revenue protected, intellectual property secured, and operational efficiency gained.
1. Minimising the Cost of Long Lifecycles
Time is the most expensive variable in a cyber incident. The global average lifecycle for a data breach is 277 days. Longer lifecycles mean higher costs. Conversely, rapid and sophisticated incident response translates into significant savings.
Companies leveraging AI and automation in Security Operations Centres (SOCs) save an average of USD 2 million compared to those without. This is not just a technology purchase; it involves developing and integrating automated detection and response algorithms—activities that often qualify for R&D tax credits globally.
2. Securing the Global Supply Chain
More than 60% of cyberattacks originate via supply chains or third‑party vendors, making supply chain resilience a critical responsibility.
Certifiable cybersecurity is becoming the new standard for B2B engagement.
- Accelerating M&A: Robust cyber due diligence prevents acquiring hidden vulnerabilities.
- Preferred Partner Status: Demonstrating a superior, globally consistent security posture differentiates companies bidding for high‑value contracts in regulated sectors such as finance, energy, and pharmaceuticals.
Pillar 2: Privacy as the Foundation of the Global Trust Economy
The fragmentation of data protection laws, from GDPR to emerging US state and APAC regulations, demands a globally consistent “Gold Standard” in privacy governance.
1. Building Enduring Customer Loyalty and Higher CLV
Consumer trust is fragile. Around 34% of consumers globally will abandon a brand if their data is misused, making privacy a direct revenue driver.
- Transparency as a Premium Service: Offer intuitive privacy dashboards that shift privacy from legal compliance to ethical partnership.
- Unlocking First‑Party Data Value: Trusted brands gain access to higher‑quality data, boosting personalisation, conversion rates and Customer Lifetime Value (CLV).
2. Driving Innovation with Privacy‑Enhancing Technologies (PETs)
Privacy regulation is not a constraint; it is a catalyst for innovation. Privacy by Design principles encourage solutions that extract analytical value while minimising exposure.
- Homomorphic Encryption: Enables computation on encrypted data without decryption.
- Differential Privacy: Adds controlled noise for aggregate analysis while protecting individuals.
- Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA): Extends «never trust, always verify» across users, devices, and applications—critical for multi‑cloud environments.
Developing and integrating these solutions often qualifies as technological R&D, making them eligible for global innovation incentives.
The FI Group Advantage: Funding the Global Security Imperative
At FI Group, we help multinationals adopt a Beyond Compliance posture while minimising net costs through R&D tax credits, grants, and innovation incentives.
The Innovation–Compliance Matrix: R&D Eligibility
| Project Activity | Technical Challenge | Eligible for R&D Funding? |
|---|---|---|
| Developing ZTA | Creating proprietary policy engines for continuous authentication | Yes |
| Data Anonymisation | Novel algorithms for GDPR‑compliant differential privacy | Yes |
| Next‑Gen Threat Detection | Training ML models for advanced persistent threats | Yes |
| Post‑Quantum Cryptography | Researching new cryptographic protocols | Yes |
| Routine Patching | Applying standard updates | No |
Actionable Roadmap: Four Steps to Global Security Leadership
- Institute a Global Data Governance Framework
Harmonise compliance across jurisdictions and map data value and risk. - Prioritise Investment in Innovation‑Qualified Security
Focus on advanced projects such as ZTA and PETs. - Cultivate Trust as a Brand Differentiator
Communicate transparently and track metrics such as CLV. - Integrate Security Spend with R&D Funding
Document technical uncertainty and partner with incentive specialists.
Organisations face a choice: treat privacy and cybersecurity as costly compliance exercises or embrace them as growth drivers and trust builders.
The businesses that dominate the next decade will be the most trusted.
By adopting a Beyond Compliance mindset and funding innovation through R&D incentives, companies secure more than networks—they secure market leadership.
Next Steps
Implementing a global Beyond Compliance strategy requires technical, financial, and regulatory expertise. FI Group offers a unified global service to align security investment with maximum innovation incentives.
In a world shaped by rapid technological change, global challenges, and shifting economic landscapes, STEM (science, technology, engineering, and mathematics) has become more than a set of academic disciplines. It is the backbone of innovation, the engine of productivity, and a strategic lever for sustainable development.
As we mark this day, it’s worth asking: what role does STEM really play in shaping our future? And how can we ensure that its benefits are accessible, impactful, and inclusive?
However, despite their transformative power, STEM fields continue to be marked by persistent gender and social disparities that limit their full potential.
Key Insights:
- STEM drives economic growth: Countries with strong STEM education and research outperform others in innovation, productivity, and GDP.
- There’s a global talent gap: Over 85 million jobs may go unfilled by 2030 due to a lack of STEM skills.
- STEM careers are evolving: AI, data science, and green technologies are reshaping the job market and requiring new skill sets.
- Access remains unequal: Socioeconomic, geographic, and demographic barriers still limit participation in STEM fields.
- Innovation needs diversity: Inclusive STEM ecosystems lead to better problem-solving, broader perspectives, and more ethical technologies.
The global challenge:
Despite its critical importance, STEM faces a global challenge: the demand for skilled professionals far exceeds supply. According to the World Economic Forum, over 85 million jobs may go unfilled by 2030 due to a lack of STEM skills. This gap threatens not only innovation but also economic resilience, especially in regions where education systems and industry are misaligned.
Moreover, access to quality STEM education and careers remains uneven. Socioeconomic disparities, geographic limitations, and systemic barriers prevent many individuals, regardless of gender, ethnicity or background, from entering or thriving in STEM fields. This imbalance limits the diversity of thought and innovation needed to solve complex global problems.
According to research by UNESCO, women represent only 28% of the STEM workforce and only 35% of STEM graduates, a figure that has remained stagnant for over a decade. In regions such as the European Union and Japan, female representation in STEM falls to 17% and 16%, respectively. Even in research and development, women represent only 31.7% of researchers worldwide, with significant regional disparities.
The numbers reflect systemic barriers, from early educational biases and a lack of role models to work cultures that hinder progress. Gender stereotypes and social expectations continue to discourage from pursuing careers in STEM, for example, despite equal or superior academic performance in many cases.
Core difficulties in STEM Fields
STEM’s potential is vast, but several structural issues persist:
- Skills mismatch: Education systems often lag behind technological advancements, leaving graduates underprepared for emerging roles in AI, data science, and green tech.
- Retention challenges: Many STEM graduates do not pursue careers in their field due to lack of mentorship, inclusive environments, or clear career pathways.
- Workforce gaps: STEM roles are growing faster than the talent pipeline can supply, especially in high-demand sectors like cybersecurity, robotics and biotechnology.
- Limited early exposure: In many regions, students lack access to STEM subjects, labs, or role models, which affects long-term engagement and career choices.
- Underrepresentation: While gender equity is improving, women, ethnic minorities, and people with disabilities remain underrepresented in STEM education and leadership.
These challenges are interconnected and require coordinated action across education, industry and policy.
The future of Innovation and Economic Growth
STEM is not just a driver of technological progress, it is a cornerstone of global economic development. Countries that invest strategically in STEM education and research consistently outperform others in productivity, innovation capacity, and GDP growth. For example, South Korea allocates over 4.8% of its GDP to R&D, leveraging its strong STEM foundation to lead in electronics, robotics and AI. Germany’s Industry 4.0 strategy integrates STEM-based automation and manufacturing, boosting industrial competitiveness and exports. In the United States, STEM-intensive sectors like Silicon Valley have created entire ecosystems of entrepreneurship, high-paying jobs and global influence.
Beyond national economies, STEM is reshaping industries. The rise of renewable energy in countries like Denmark and Germany is powered by STEM-trained engineers and scientists developing wind, solar and smart grid technologies. In biotechnology, nations like China and Singapore are investing heavily in genomics and personalised medicine, creating new markets and improving public health outcomes.
As we look ahead, STEM will continue to be the foundation for solving global challenges, from climate change and food security to digital transformation and ethical AI. The future belongs to those who can innovate responsibly, adapt quickly and collaborate across disciplines.
Top STEM trends to watch in the coming years
- AI and Machine Learning Integration: AI will become ubiquitous across industries, with growing demand for specialists in explainable AI, algorithmic ethics and human-AI collaboration.
- Green and Sustainable Technologies: STEM will drive innovation in clean energy, carbon capture, circular economy design and climate modelling.
- Quantum Computing and Advanced Materials: Breakthroughs in quantum systems and nanomaterials will unlock new possibilities in computing, medicine and manufacturing.
- Biotech and Personalised Health: Genomics, microbiome research and bioengineering will transform healthcare, enabling tailored treatments and predictive diagnostics.
- Cybersecurity and Data Ethics: As digital systems expand, STEM professionals will be essential in securing infrastructure, protecting privacy and ensuring ethical data use.
- Space and Deep Tech Exploration: Roles like space architects and planetary engineers will emerge as lunar and Martian missions become reality.
- STEAM and Interdisciplinary Innovation: The fusion of arts and STEM will foster creativity, design thinking and holistic problem-solving in education and industry.
- AI-Powered Education and Lifelong Learning: Adaptive learning platforms, micro-credentials and hybrid models will redefine how STEM skills are taught and acquired.
As we look to the future, STEM will remain the cornerstone of innovation, economic resilience and global problem-solving. Its influence spans industries, borders and generations, from powering green technologies and personalised healthcare to securing digital infrastructure and exploring deep space. The nations and organisations that invest in STEM today are not only preparing for tomorrow’s challenges; they are actively shaping the solutions.
To unlock its full potential, we must continue to align education with industry needs, foster inclusive ecosystems, and promote lifelong learning. STEM is not just about science and technology, it’s about building smarter economies, more equitable societies and a future defined by purpose-driven innovation.
How Space Technology Can Accelerate Net Zero Goals
Space-based technology has become one of the most powerful tools in tackling the global challenge of climate change and decarbonisation. From Earth observation satellites that monitor greenhouse gas emissions to advanced propulsion systems that reduce launch footprints, innovation in space technology is critical to achieving net-zero targets.
For SMEs and scale-ups in Europe and the UK, this sector offers a dual opportunity: driving technological breakthroughs while accessing substantial public and private funding. Yet navigating this landscape requires strategic insight. Each scheme has unique compliance demands, funding structures, and cross-border implications, and CFOs face increasing pressure to align innovation spend with decarbonisation goals while ensuring strong ROI.
This article provides a comprehensive roadmap of the funding available across Europe and the UK, from the European Space Agency (ESA) to Horizon Europe and national schemes. It also highlights the CFO pain points in financing innovation, and explains how FI Group’s “Global Reach. Local Expertise.” approach enables clients to maximise returns while reducing compliance risks.
Comparison of Major Funding Programmes
| Programme | Budget (2021–2027) | Focus Areas | Typical Funding Size | Relevance to Space Decarbonisation |
| Horizon Europe | €95.5bn | Climate, Energy, Digital, Space | €500k–€15m | Collaborative R&D, space-enabled sustainability |
| EIC Accelerator | €10bn (subset of Horizon) | Deep-tech, disruptive innovation | Up to €2.5m grant + €15m equity | Hardware/software scale-ups in climate & space |
| ESA Clean Space | €180m+ since 2010 | Green design, debris mitigation | €50k–multi-million | Clean propulsion, eco-satellites, reusability |
| LIFE Programme | €5.43bn | Environment & climate action | €1m–€10m | Climate services, space-enabled adaptation |
| UK Space Agency | £100m+ annual calls | Space science, sustainability | £50k–£15m | National missions (e.g. CO₂ monitoring) |
| Innovate UK Net Zero | £1bn+ portfolio | Clean energy, mobility, data | £50k–£2m | Satellite data for net-zero mobility, energy |
What is Space Technology for Decarbonisation?
Space technology for decarbonisation refers to the application of space-based tools and services to reduce carbon emissions, improve resource efficiency, and accelerate the transition to net-zero economies. Examples include:
- Earth Observation: Satellites providing real-time data on emissions, deforestation, and ocean health.
- Green Propulsion: Development of non-toxic, sustainable fuels for satellites and launchers.
- Energy Infrastructure: Space-based solar power and satellite-enabled grid optimisation.
- Supply Chain Monitoring: Using satellite data to verify carbon reduction claims in global trade.
- Climate Modelling: Advanced sensors that feed into predictive models for policymakers and businesses.
This convergence of space, sustainability, and digital technology creates new commercial opportunities but requires significant upfront investment, hence the growing importance of grant funding and R&D tax incentives.
Why CFOs Must Pay Attention
CFOs in innovation-driven SMEs face three recurring challenges:
- Balancing long-term innovation with short-term cash flow
Developing decarbonisation tech often requires large upfront spend on prototypes, testing, and compliance, with delayed revenue realisation. - Navigating fragmented funding ecosystems
EU, ESA, Innovate UK, and private funds all have different eligibility rules, reporting standards, and audit risks. - Avoiding opportunity costs
Missing out on grants or misaligning R&D incentives across borders can cost millions, not just in lost funding, but in lost competitive advantage.
In a climate where venture capital funding has declined year on year since 2021, grants and tax incentives are becoming the most reliable growth levers for high-tech firms.
Funding Opportunities in Europe
European Space Agency (ESA)
The ESA runs multiple programmes aligned with sustainability and space innovation:
- ESA’s ARTES (Advanced Research in Telecommunications Systems) – supports SMEs developing satellite-enabled services for climate monitoring, smart cities, and mobility.
- ESA Clean Space Initiative – focuses on eco-design, debris mitigation, and clean propulsion.
- ESA Technology Development Element (TDE) – funds feasibility studies and prototypes with applications in decarbonisation.
ESA grants often require international collaboration, making FI Group’s network across 13 countries a decisive advantage in forming and managing consortia.
Horizon Europe
With a €95.5 billion budget (2021–2027), Horizon Europe is the EU’s largest funding programme for research and innovation. For space decarbonisation, key clusters include:
- Climate, Energy & Mobility – funding projects in clean aviation, sustainable fuels, and renewable integration.
- Digital, Industry & Space – supporting satellite manufacturing, AI-driven Earth observation, and next-gen propulsion.
- Missions on Climate-Neutral Cities and Oceans – creating opportunities for space-enabled monitoring solutions.
The European Innovation Council (EIC) Accelerator within Horizon Europe also offers up to €2.5 million in grants plus blended finance, particularly relevant for scale-ups in green and space technologies.

Other EU Initiatives
- LIFE Programme (€5.43bn): Focused exclusively on environment and climate action.
- Clean Hydrogen Joint Undertaking (Clean H2 JU): €2bn for hydrogen innovation, often linked with space propulsion and storage systems.
- Digital Europe Programme (€7.59bn): Funding for AI and cybersecurity in satellite data processing.
Funding Opportunities in the UK
Innovate UK
The UK’s national innovation agency Innovate UK regularly opens competitions relevant to space and decarbonisation, such as:
- National Space Innovation Programme (NSIP) – supporting space data and climate applications.
- Net Zero Mobility and Aviation Calls – investing in clean propulsion and aircraft electrification.
- Smart Sustainable Plastic Packaging – relevant for supply chains where satellite monitoring validates sustainability claims.
UK Space Agency
Through targeted calls, the UK Space Agency co-funds ESA projects and runs initiatives on space debris mitigation and low-carbon satellite technologies.

Combined Approach: R&D Tax Relief + Grants
For UK SMEs, R&D tax relief remains a crucial complementary mechanism. Costs not covered by grants can often be claimed under the merged R&D Expenditure Credit (RDEC) scheme, offering a ~20% taxable credit on qualifying costs. CFOs must carefully structure projects to avoid “double-dipping”, where the same cost is claimed twice under different schemes, a compliance risk that FI Group’s integrated advisory model helps mitigate.
Private and Venture Funding Landscape
While venture capital remains the largest pool of growth finance, the market has cooled significantly since 2021. UK deal volumes have fallen, though average deal sizes remain larger than a decade ago, with deep-tech and life sciences attracting outsized interest.
For space decarbonisation, this means CFOs should see public funding as a hedge against VC volatility. Grants de-risk early-stage projects, making companies more attractive to private investors down the line.
Roadmap for SMEs and Scale-Ups
For SMEs considering entry into the space decarbonisation ecosystem, a structured roadmap is critical:
- Map Your Innovation Pipeline
Identify which projects align with decarbonisation priorities (e.g. propulsion, data analytics, monitoring). - Select the Right Funding Mix
Combine grants, R&D tax relief, and where possible, blended finance instruments. - Form International Consortia
Particularly for Horizon Europe and ESA projects, partnerships improve eligibility and competitiveness. - Align Reporting and Compliance
Different jurisdictions have different audit risks; early planning avoids costly delays. - Leverage Expert Support
Engage advisors who understand both the technical innovation and the financial compliance.
The FI Group Advantage
At FI Group, we turn complexity into clarity for innovation leaders. With over 1,400 experts across 20 countries, we support more than 15,000 clients annually, securing over €1.7bn in funding.
Our advisory goes beyond funding applications. We help CFOs and executives:
- Mitigate compliance risk by ensuring claims are audit-ready across jurisdictions.
- Optimise funding strategy through a single-point-of-contact model.
- Accelerate international expansion, bridging HQ strategy with local execution.
As Dr. Fawzi Abou-Chahine, Funding Director at FI Group UK, explains:
“We support clients to navigate the most competitive EU and UK schemes. Our role is not just to write applications, but to align funding with strategic goals, whether that’s scaling internationally, strengthening IP portfolios, or accelerating net-zero innovation.”
International Landscape: Global Reach, Local Expertise
Innovation does not stop at borders. Space and decarbonisation projects often require cross-continental collaboration, from launch facilities in South America to data analytics hubs in Europe and Singapore.
FI Group’s model ensures that:
- Your HQ sees the full picture, while your teams feel local support.
- Global operations don’t need global headaches.
- We deliver seamless international compliance, reducing risk in multi-country claims.
This capability is critical during M&A, supply chain shifts, and expansions where funding incentives vary widely across jurisdictions.
FAQs
What is the main funding source for space decarbonisation projects in Europe?
The European Space Agency and Horizon Europe are the leading sources, with additional opportunities under LIFE, Clean Hydrogen JU, and Digital Europe.
Can SMEs combine R&D tax relief with grant funding?
Yes, but careful structuring is needed to avoid claiming the same cost twice (“double-dipping”). FI Group helps ensure compliance with HMRC and EU rules.
How competitive are Horizon Europe calls?
Horizon Europe success rates average 10–15%, but consortium-based applications led by SMEs with strong partners see higher success.
What are CFO pain points in managing international incentives?
CFOs struggle with fragmented regulations, audit risk, and inconsistent reporting across jurisdictions. Integrated advisory support mitigates these challenges.
Why work with FI Group?
Because we combine global scale with local expertise, securing over €1.7bn in funding annually and offering tailored support for space and decarbonisation innovators.
IT innovation isn’t limited to the digital sphere. Increasingly, industrial applications of technology are pushing the boundaries of what’s considered R&D.
When businesses use technology to solve operational, logistical, or energy challenges in new ways, they’re often venturing into innovative territory.
Some examples might include:
- AI-powered logistics route optimisation based on real-time conditions
- Development of smart warehouse automation tools
- Creation of new communication devices for confined or hazardous environments
- Software platforms managing energy distribution via smart grids
- Predictive systems for inventory management based on dynamic variables
- Advanced tools for risk modelling and pricing analysis
- User behaviour analytics that predict purchase likelihood or engagement patterns
In these cases, the technology isn’t just supporting the business, it’s reshaping how the business operates, opening the door to R&D qualification.
What Exactly Counts as R&D?
At its core, R&D is about creating value through new knowledge or novel applications of existing knowledge.
Projects generally fall into one of three key categories:
- Scientific Research: Activities that generate new knowledge, whether through fundamental or applied exploration.
- Technological Development: Projects that translate knowledge into concrete solutions, products, or prototypes.
- Technological Innovation: Significant improvements or entirely new methods, processes, or systems, often involving novel technologies or methodologies.
While these categories may sound academic, the reality is that many IT and digital transformation projects can fall within their scope.
Where Tech Meets R&D: Common Eligible IT Initiatives
Digital innovation is a fast-moving field, and many solutions that tackle complex challenges could meet the criteria for R&D recognition.
For instance:
- AI systems used for fraud detection or risk assessment
- Implementation of advanced frameworks to improve software performance
- Blockchain technologies ensuring data transparency and traceability
- Immersive tech applications in industrial or training environments
- Predictive analytics or machine learning models based on real-time data
- Automated asset management and intelligent resource planning
- Cloud-based cybersecurity solutions beyond traditional perimeter defences
- Algorithm development and mathematical modelling for smart engines
- Scalable cloud platforms tailored to new services or users
- Innovative approaches to integrated delivery management
These aren’t just examples of digital progress, they’re potential R&D projects with real business impact and tangible fiscal benefits.
Hispanic America as a case study: Tax Incentives in Peru
In a world where innovation drives competitive advantage, research and development (R&D) is no longer a luxury, it’s a strategic position.
Around the globe, companies are investing in knowledge-based growth to stay ahead of the curve. In Peru, this global trend is taking on a particularly promising form: tax incentives designed to encourage and reward innovation.
But how do you know if your project qualifies?
Could your next technology initiative not only advance your operations but also reduce your tax burden?
The R&D Advantage: A Strategic Incentive
The power of innovation to shape sustainable economic development must be recognised, and in the case of Peru, for example, a specific tax incentive has been introduced:
- Law No. 30309: companies that invest in scientific research, technological development and technological innovation projects can deduct the expenses incurred on their tax return.
This innovative regulation offers additional income tax deductions to companies that invest in scientific research, technological development or technological innovation.
It’s not just about rewarding great science or complex engineering, it’s about promoting a culture of innovation in which experimentation, development and improvement are actively supported.
Do you have questions about whether your project can qualify for the R&D criteria?
Here are some questions we suggest you ask yourself:
– Are you solving a technical problem with no clear solution at the outset?
– Does it involve a significant advance in either what is being done or how it is being done?
– Are you experimenting with untested ideas or developing new methodologies?
– Is there a measurable element of uncertainty or technical risk?
– Will you generate knowledge that did not previously exist in your company, sector or region?
– Are you applying existing technologies in innovative ways?
If you can confidently answer ‘yes’ to several of these questions, there’s a good chance your project will qualify, and it may be time to explore your eligibility for R&D tax benefits or other innovation-centred incentives.
With a global vision and clients around the world, FI Group specialises in the technical and legal criteria of R&D classification, monitoring the entire process. Our teams of experts combine technical knowledge and strategic vision to ensure that your projects meet the necessary standards and have the best chance of success.
Remember: your innovation today can generate tax benefits tomorrow.
Artificial intelligence has never been more integrated into daily life and business world. Since the launch of ChatGPT in 2023, the number of companies adopting AI has jumped by 20%, reaching 78% of all organisations questioned in the «State of AI: Global Survey» by McKinsey & Company.
Clearly, AI is no longer just an optional tool; it’s becoming an essential strategic asset for companies aiming to stay competitive and innovative. But as businesses invest efforts into AI, they also face a subtle but significant risk: cognitive debt. According to recent MIT research (2025), overreliance on AI can erode essential human skills like creativity and critical thinking.
So how can companies harness the power of AI without compromising their greatest resource: their people?
Accelerating Innovation with AI
AI is often associated with boosting operational efficiency, but its potential goes far beyond that. It can significantly accelerate innovation across every stage of the R&D process, from generating ideas and prototyping to testing and launching new products.
Traditionally, innovation was slow, costly, and limited by human resources and physical experimentation. Now, AI lets companies rapidly run thousands of simulations and test numerous hypotheses at once, tasks that used to take months or years can now be completed in days or even hours.
For instance, pharmaceutical giants like AstraZeneca have partnered with AI startups such as BenevolentAI to quickly screen millions of chemical compounds. This collaboration has dramatically shortened the drug discovery timeline, bringing new treatments to market much faster. AI’s ability to analyse huge datasets and detect meaningful patterns also improves decision-making, ensuring companies invest their R&D budgets wisely.
According to Gartner (2024), companies that integrate AI-driven analytics into their research can more accurately predict market trends, customer preferences, and technological feasibility. Brands like Unilever and Procter & Gamble use AI analytics to better anticipate consumer trends, aligning their innovation strategies closely with market demands.
The Hidden Risk: Cognitive Debt
Despite its undeniable advantages, AI also presents hidden risks.
A recent MIT study, «Your Brain on ChatGPT» (Kosmyna et al., 2025), highlighted that excessive reliance on AI can reduce brain activity linked to creativity, critical thinking, and memory. Participants who regularly depended on AI exhibited weaker cognitive engagement and poorer recall compared to those who completed tasks without AI. This phenomenon, known as «cognitive debt», occurs when individuals consistently outsource mental tasks to technology, gradually weakening their own cognitive abilities. Though AI streamlines workflows, excessive reliance can unintentionally undermine the very human qualities that drive sustained innovation.
Balancing AI and Human Potential: Practical Strategies
To fully realize AI’s benefits while avoiding cognitive debt, businesses should consider these best practices:
- Complementary use of AI: Encourage teams to see AI as an enhancer of human capabilities rather than a substitute.
- Continuous learning: Invest in training programs that simultaneously develop critical thinking, creativity, and technological proficiency.
- AI Governance: Create clear guidelines on ethical AI use, transparency, and human oversight, as recommended by authorities such as McKinsey and Harvard Business Review (2024).
By implementing these strategies, businesses can leverage AI effectively while preserving and enhancing their human capital.
Navigating the AI Revolution Thoughtfully
AI presents tremendous opportunities for accelerating innovation, increasing efficiency, and creating lasting competitive advantages. Yet, as businesses embrace AI, maintaining awareness of cognitive risks remains crucial. The smartest path forward involves strategically balancing AI’s powerful capabilities with the irreplaceable creativity and ingenuity of human talent.
Companies that master this balance will lead the future, strategically integrating AI to unlock sustained innovation and growth.
Did you know that over 70% of companies worldwide are already using some form of artificial intelligence in their processes? Currently, AI is not only transforming industries but also changing the way teams work and add value.
At FI Group, we have made artificial intelligence an ally to enhance our internal capabilities, improve our efficiency, and deliver better results for our clients.
The integration of AI into our daily work allows us to:
- Automate routine tasks: Automation through AI can save up to 30% of time on administrative and management activities
- Prioritize what really matters: By letting AI handle low-value tasks, our team can focus on strategic and creative projects that generate real impact for our clients.
- Quickly access and process key information: With the help of MarIA, our integrated artificial intelligence tool, we can analyze large volumes of documents and access cross-sectional information about our clients and the company to process and obtain relevant information in minutes.
- Improve decision-making: A recent IBM study reveals that 42% of consulting firms already use AI to support decision-making and real-time data analysis
How We Use AI at FI Group
The implementation of AI at FI Group spans several key areas that have transformed our daily operations:
- Support for teams: Tools like MarIA, SmartRead, and Copilot interact with each employee, assisting in document management and answering operational questions. This facilitates a review of the state of the art with an academic database, allowing human talent to focus on developing high-value information for the process.
- Process automation: The digitization of tax documentation has become a quick and efficient task thanks to tools like the invoice scanner, which uses locally trained AI. This not only speeds up document analysis but also improves efficiency in responding to our clients.
- Continuous learning: AI is not static; it learns from our processes and provides teams with personalized suggestions, helping to improve every day. This cycle of continuous learning is essential for adapting to the changing needs of the market and our clients.
For the successful integration of AI, it is essential to consider several aspects:
- Organizational culture: We are committed to the ongoing training and updating of our team. Training focuses not only on the use of tools but also on understanding how AI can enhance our capabilities.
- Ethics and responsibility: At FI Group, we ensure the safe and ethical use of data, protecting the confidentiality of our clients’ information. Trust is a fundamental pillar in our relationship with them.
- Long-term vision: We see AI as a tool to enhance human value, not to replace it. Our focus is on how artificial intelligence can complement and improve human work, creating synergies that benefit both our employees and our clients.
Artificial intelligence is a fundamental part of our operational strategy. It allows us to be more agile, respond better to our clients’ needs, and find new ways to deliver real value in a competitive environment. Our experience shows that when AI is integrated with a human and orderly vision, the results multiply.
In a world where innovation is the key to surviving and thriving, artificial intelligence is not just a tool but a strategic partner. By adopting AI responsibly and ethically, we not only optimize our processes but also open the doors to a future full of possibilities. Companies that dare to integrate AI into their DNA not only stay at the forefront of innovation but also become leaders in their respective sectors, creating a lasting impact on society and the economy.
The AI-driven transformation is a continuous journey. At FI Group, we are committed to continuing to explore new applications and improvements in our artificial intelligence tools, ensuring that every day we can provide an even more efficient and valuable service to our clients. Artificial intelligence is the path to a brighter and more productive future, and we are excited to be part of this revolution.
In recent years, the intersection of technology, medicine, and healthcare has created an environment ripe for innovations that transform how we manage our health and interact with medical services. Over time, the healthcare sector has increasingly absorbed technological advances and applied them within the field – and this relationship has opened the way for a powerful strategy known as cross-industry collaboration, where different sectors come together to share knowledge, experience, and technology, resulting in two distinct strands: HealthTech and MedTech.
What is meant by cross-industry?
In many cases, an innovative solution developed in one industry can serve as an effective remedy for challenges faced in another sector. This is the essence of the cross-industry approach: a strategic method that encourages the exploration of hybrid solutions by fostering collaboration between companies from diverse fields.
By leveraging unique insights and technologies from various industries, this approach aims to catalyse innovation, accelerate growth, and uncover a wide range of tailored solutions. These collaborations can create mutually beneficial opportunities, driving value for all parties involved while pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in their respective domains.
MedTech & HealthTech
According to the World Health Organisation (WHO), healthcare can be defined as «the application of organised knowledge and skills in the form of devices, medicines, vaccines, procedures, and systems developed to address health problems and enhance the quality of lives.”
Even with the terms HealthTech and MedTech often used synonymously, they serve distinct purposes in the healthcare ecosystem. HealthTech solutions are more concerned with leveraging technology to augment the overall healthcare experience for patients, including innovations that enhance telehealth platforms, mobile health applications, and data analysis tools that allow patients to monitor their health in real time, thereby empowering them to take an active role in their health journey.
MedTech solutions, on the other hand, are focused on advancements in medical treatment and diagnostic processes. This encompasses improvements in diagnostic efficiency and accuracy, as well as the design and development of state-of-the-art medical devices, surgical tools, and patient monitoring systems. MedTech innovations particularly cater to healthcare professionals by providing them with the tools necessary for effective patient diagnosis and treatment.
A simplified distinction can thus be established: MedTech focuses on the development and application of technologies aimed at managing healthcare and enhancing diagnostic capabilities, while HealthTech prioritises the creation of tools and systems that enhance the patient experience and support consumer engagement in their own health management.
Examples of technologies in the health sector and their uses
With these differences established, we can now cite some examples illustrating the impact of various technologies in the health sector that have affected – and revolutionised – medical practices and the general day-to-day lives of patients around the world:
1. Neurotechnology
Neurotechnology has existed in the medical realm for some time, yet continues to progress in astonishing ways. It includes both implantable and external devices, covering all elements designed to comprehend brain functions. With the aid of these technologies, we can visualise the workings of the human brain and control, repair, or enhance its operations.
Neurotechnology components can include computers, electrodes, and other devices that interpret electrical impulses. At this moment in time, neurotechnology is utilised for various processes such as:
- Brain imaging: capturing magnetic fields generated by the brain’s electrical activities
- Neurostimulation: activating the brain and nervous system to influence brain functions
- Neuro-devices: devices employed to monitor and regulate brain activities, using implants
2. Telemedicine and telehealth
Telemedicine has grown rapidly in recent years, and many health systems now use it. It benefits both patients and healthcare workers: for patients, telemedicine offers convenience, making it easier to access care, save money, avoid travel expenses – and the risk of missing work for in-person visits. For healthcare professionals, it lowers costs and limits their exposure to illness, while also allowing them to see more patients with greater flexibility.
3. Wearable technology
Wearable technology, commonly referred to as wearable tech, encompasses a range of devices designed to track various health metrics, such as monitoring the heart rate in real-time, analysing sleep patterns to assess sleep quality, measuring blood pressure, and even tracking physical activity levels such as the number of steps taken and calories burned. On top of that, many models incorporate features like GPS tracking for outdoor activities, stress management tools, and reminders for hydration and movement. As health awareness grows, these devices have morphed from mere novelties into essential tools for many, aiding users in achieving their fitness goals and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
4. Robotics in surgery
These advanced technologies support surgeons in performing minimally invasive procedures with remarkable precision and agility. They not only simplify straightforward surgical procedures, but also enable the performance of more intricate operations, thus enhancing the overall effectiveness and outcomes of medical interventions. By providing a steady hand and clear visual field, they permit surgeons to navigate complex anatomical structures with confidence and skill.
As these technologies continue to evolve, collaboration across industries will become ever more crucial. This synergy will not only drive innovation but also create a more efficient, personalised, and patient-centric healthcare ecosystem. The success of this collaborative approach can lead to a future where healthcare is more accessible, effective, and tailored to individual needs, promoting lasting well-being for all.
Key Takeaways
- Cross-industry collaboration is a strategy that fosters the exchange of knowledge and technologies, enabling the exploration of hybrid solutions that can solve challenges across industries.
- Examples of technologies that have revolutionised healthcare include neurotechnology, telemedicine, wearable technology, and surgical robotics, each contributing in distinct ways to the care provided and its management.
- Cross-sector collaboration can create a more accessible and efficient healthcare system, enabling patients to take an active role in their health and providing professionals with the necessary tools for effective diagnosis and treatment.
- The synergy between technology and healthcare promises a future where care is more personalised and tailored to individual needs, promoting lasting well-being for all.
In a dynamic and competitive world, access to information is crucial for business success. Companies that want to stand out need to go beyond simply collecting data by turning them into actionable insights that drive the growth and profitability of their business. It is in this context that business intelligence (BI) becomes an essential tool.
What is Business Intelligence?
Business intelligence is a set of processes, technologies and tools that transform raw data into strategic information to help companies make assertive decisions.
By collecting, organising, analysing and visualising data from various sources, BI provides managers with a complete and comprehensive view of their organisation’s performance, allowing them to identify opportunities, optimise processes, reduce costs, increase efficiency and make smarter decisions to achieve strategic objectives. This article provides an introduction to BI, but it can only cover the tip of the iceberg.
Traditional business intelligence emerged in the 1960s as a system for sharing information within organisations. In the 1980s it developed alongside computer models to aid decision-making and transform data into information. Modern BI solutions prioritise governed data on reliable platforms, the autonomy of business users, and fast access to information.
What are the Advantages of Business Intelligence for Business?
More and more people generate and/or create data every day, making the latter ever more diverse and unstructured.
In this sense, and once we know what business intelligence is, a careful use of the BI approach can help any organisation gain a competitive advantage by reducing the time and effort needed to acquire, integrate, distribute, analyse and respond to new data.
The better a company’s data processing is, the more it will benefit from BI. In fact, the leaders in data processing exert enormous pressure on all competitors who fail to recognise the potential of their data in good time. Late adopters are forced to accelerate their analytical ambitions to keep up with competitors and new market entrants.
BI is thus right at the core of all data-driven companies, making it the epicentre of their transformation. The implementation of new BI tools is aimed at boosting an organisation’s impact and rendering it more efficient. But with the right BI technology, you can also gain a number of additional benefits.
These include:
- Higher efficiency of operational processes
- Insights into customer behaviour and buying patterns
- Precise control of sales, marketing and the financial performance
- Clear reference points based on historical and current data
- Instant alerts on data anomalies and customer problems
- Analyses that can be shared in real time between various departments
In the past, business intelligence tools were mainly used by data analysts and IT users. But nowadays, BI platforms make business intelligence available to everyone, from executives to operations teams.
To this end, FI Group has launched a new digital space that integrates several applications in a single platform. This way our clients can benefit from greater transparency about the services they develop with us.
For the future, it is vital that the people and companies around us adapt and use new digital resources to reach their full potential, converging on innovative and exciting ideas.
FI Connect
FI Connect is a HUB of digital applications created by the FI Group to transform, automate and optimise our customer relationships.
This suite of applications enables FI Group to offer a more structured consultancy support, making our clients’ lives easier and letting them focus on their R&D projects by ensuring better communication and greater efficiency in our delivery of their R&D claims.
Business Intelligence Applications
The versatility of Business Intelligence allows it to be applied across various sectors and areas of activity within a company. Some examples of how BI can be used to generate value in different sectors include:
Sales and Marketing
- Analysis of marketing campaigns to identify the most effective ones and optimise marketing investments
- Analysis of customer behaviour to understand their preferences, needs, and buying journey
- Market segmentation to target campaigns and offers more precisely and effectively
- Defining competitive prices based on market data and competitor analysis
Finance
- Cost and profitability analysis to identify areas for optimisation and improving profit margins
- Cash flow monitoring to ensure the company’s financial health and make more informed investment decisions
- Investment analysis to assess returns on investment and make more strategic decisions
- Forecasting of financial trends to prepare for future events and mitigate risks
Operations
- Production monitoring to identify potential adversities and improve operational efficiency
- Quality control to ensure that products meet the required quality standards
- Stock management to optimise stock levels and reduce costs
- Logistics optimisation to reduce transport and delivery costs
Human Resources
- Analysis of performance indicators to assess employee performance and identify areas for training and development
- Talent retention to identify key turnover indicators and implement retention programs
- People development to identify the skills and knowledge needed for the company’s success, and invest in employee development
Customer Service
- Analysis of customer feedback to identify areas for improvement and enhance the customer experience
- Resolving problems quickly and effectively to shorten resolution times and increase customer satisfaction
- Optimisation of service channels to direct customers to the most appropriate channel and reduce costs
The provision of reliable information for making strategic decisions, to optimise processes, reduce costs and increase competitiveness makes BI a crucial differentiator for companies wishing to stand out in an increasingly competitive and dynamic market.
Investing in a business intelligence solution is an investment in your company’s future.
Share this article on business intelligence with your network of contacts. Explore FI Group’s article archive to find more related and relevant content.
What is Data Privacy?
Data privacy is the principle that allows an individual to have control over their personal data, including the ability to decide how organisations collect, store, and use such information.
Data privacy is not only crucial to prevent unauthorised access and misuse of information, but also strengthens the trust between consumers and businesses in an increasingly interconnected environment.
Why is it Important?
In an increasingly digitalised world, protecting personal data has become crucial to ensure the security and privacy of individuals. Data privacy ensures that our data is secure and used only for authorised purposes, providing peace of mind in the digital world.
How can Companies Protect their Data?
At the business level, data protection and privacy now number among the main objectives. Companies are putting all their efforts into ensuring this protection, as well as ensuring compliance with the GDPR.
This compliance is achieved by the implementation of policies that establish procedures for data protection. Additionally, technical measures are increasingly aimed at ensuring information privacy.
The most common technical measures applied by companies include the use of multi-factor authentication to manage access, systems that prevent and detect intrusions, and data encryption to ensure their immutability.
In addition to that, these measures need to be evaluated and audited periodically, and continuous training of personnel in privacy matters is necessary. This will allow us to ensure GDPR compliance, thereby reinforcing our customers’ trust.
What are the Challenges of the Future?
The main challenge for FI Group in 2025 regarding data privacy is the use and management of AI. It is crucial to adopt measures that allow us to ensure the responsible development and use of AI, thereby guaranteeing that the rights of the individuals concerned are respected. On the occasion of Data Protection Day (January 28), we therefore take the opportunity to remind you that at FI Group, we are committed to developing and using innovative practices that help us drive progress.
These measures need to ensure the security and privacy of our data, which is why it is everyone’s job to follow these good data protection practices.
How Does FI Group Protect Its Data?
FI Group recognizes the importance of safeguarding data, both our own and that of our customers. Therefore, we implement security measures designed to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of this data.
We rely on four key strategies to establish these measures:
- Privacy by Design: We ensure that data privacy is integrated from the initial design phase of any process.
- Advanced Security Measures: We utilize advanced cryptographic techniques and the latest technologies to protect our systems and processes from threats.
- Awareness: We provide resources and training to help our employees understand their rights and responsibilities regarding data protection.
- Compliance: FI Group adheres to global policies and local data protection regulations, ensuring a consistent level of protection.
Grants and financial instruments
Grants are defined as a type of funding typically available to beneficiaries after successfully submitting an application related to a “call for proposals” managed by the EU, national or regional authorities. Grants can take various forms, e.g. as a reimbursement of eligible costs, of unit costs, as lump sums, flat-rate financing, or also a combination of these. Most EU grants are provided as co-financing so beneficiaries need to come up with at least half the necessary resources themselves.
Financial instruments are defined as funding provided in partnerships involving public and private institutions (e.g. under the EU shared management funds) in the form of loans, guarantees, equity, or quasi-equity. The main benefits of the financial instruments include that the money repaid by final recipients can be reused to support further investments (revolving effect), that additional public and private co-investments are potentially attracted (leverage effect), the nearness to the market, and their implementation by financial intermediaries contributing their own sector expertise (high impact).
A combination of grants and financial instruments can be of major help for the growth of startups, SMEs and other businesses, but also the realisation of policy objectives on a national or EU level, and address market failures related to a project’s viability and access to finance. The potential benefits of such combinations can for example include additional support, overcoming financial shortfalls where investments are unable to make enough profit or too risky for private investors, and a higher impact thanks to economies of scale.
Grant + equity schemes
Research and innovation (R&I) are crucial for the sustainable success and growth of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in the EU. These make up 99% of all EU businesses, create ca. 100 m jobs, and are an essential source of entrepreneurship and innovation, both of them of crucial importance for the EU’s competitiveness.[1] The definition as an SME or startup is important for the access to finance and EU support programmes intended specifically for them[2]. SMEs and startups operate in a rapidly evolving and challenging environment that calls for investment and adherence to standards and regulations, also in light of their limited skills and financial resources.
Financial markets often fail to provide SMEs and startups with the funding they need. Horizon Europe, the EU’s R&I funding programme scheduled until 2027 involves the European Innovation Council (EIC), which supports game-changing innovations throughout the life cycle of start-ups and SMEs, from early research via the funding through to the scaling up, with a budget of EUR 10.1 bn.
The EIC provides funding by way of grants and investments both. The investments currently take the shape of direct equity or quasi-equity investments and are managed by the EIC Fund, whose main investors include the European Commission and European Investment Bank (EIB). One of the three funding and support options available in the EIC Work Programme 2024 is the EIC Accelerator designed to support SMEs, start-ups, spin-offs, and in exceptional cases also small mid-caps, in the development phase of products or services, in bringing their innovations to market and scaling them up where the risk involved is too high for private investors to provide all the required funding. Up to €2.5 m are available in grants for innovation activities, and up to €15 m in equity investments for the market launch and scale-up, all from the resources of the European Investment Bank (EIB). This new model now offers greater funding diversity and additional flexibility for the timing of investment support, permitting applicants to make separate decisions about the forms of funding in line with their company’s investment needs, market developments, and opportunities for attracting co-investors.
The most popular option is applying for blended finance, a combination of grant money and equity investment that must be defined at the time. Next come grants as initial funding, leaving the option to go for equity investments at a later stage, usually once the technology being developed has reached specific milestones. This blending model involving a mix of subsidies + equity for companies in need of funding is a good example for SME and startup support schemes in the growth and scale-up phase.
Grant + loan schemes, European Investment Fund, loans and micro-loans
The EIF oversees several mandates on behalf of the European Commission as well as national and regional managing authorities. Instead of the EIF providing funding or guarantees to individuals or companies directly, the final funding approval is the sole competence of the financial intermediary on a national level. The loans provided by the EIF can also be combined with funding from other EU sources (e.g. the EU budget), in a process known as blending.
For large companies, the EIF will cover investment costs (typically for a period of up to three years, but possibly longer), e.g. for research and development or the costs of facilities or activities, up to 50% of total project costs. These loans typically start at €25 m, but the EIF will also consider lower amounts in specific cases. This blending model involving a mix of grants + loans for companies in need of funding is a good example for profitable investment support schemes where businesses require liquidity to start investments capable of generating revenues that will enable them to repay their loans.
Combined RDI loans in Spain on a national level
A specific example of grant and loan combinations is provided by Spain’s combined RDI loans, which are overseen by the Spanish Centre for the Development of Industrial Technology (CDTI).
This scheme foreseen a partly repayable loans (long terms loans at fixed interest rate below the market standards which include one part that should not be reimbursed) funded by central state budget resources. The aid intensity is up to 85% of the approved budget and the non-refundable component is between 10% and 33% of the aid. This combination could be implemented with EU funds in the 2021-2027 period, provided all other Common Provision Regulation (Regulation (EU) 2021/1060) rules are respected, (loan financial instrument cannot be used to pre-finance grants and grants cannot be used to repay the loan financial instruments).
[1] Source: European Commission – Internal Market, Industry, Entrepreneurship and SMEs.
[2] Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) are currently defined in EU recommendation (N.2003/361).
FI Testimonials is an FI Group campaign featuring a series of interviews in which we delve into how we assist our clients in nurturing their ideas and share our customers’ perspectives on our services. Through their testimonials, we explore various companies from diverse sectors as they share their innovation projects, the challenges they face, and how collaboration with FI Group has helped them achieve their goals.
Our first video features Leanbio, a biopharmaceutical CDMO, we had a conversation with their CEO, Albert Font, who shared insights about the company’s present and future. Have you heard about development of biologic products before?
Read the full interview below.
What is Leanbio?
I am Albert Font and I am the CEO of Leanbio. Leanbio is a Biopharmaceutical CDMO, which means we offer biologics development and manufacturing services. We also specialise in recombinant proteins, plasmic DNA and MRNA.
We are a company with a global scop and our main objective is to make the journey as easy as possible for our clients, from the initial stages until the product reaches the market.
Leanbio currently has almost 400 square metres in the Barcelona Science Park. They are distributed in laboratories dedicated to process development, analytical methods development and quality control. We also have different pilot plants to provide services up to toxicological studies. And we are currently expanding our production capacity in a new production facility that will be almost 4000 square meters in size, with three main production lines: one based on microbial expression systems, one based on cell cultures and then also we’ll have some dedicated rooms to making MRNA-based products.
Apart from these three main production lines, we will have different services like quality control to release the product and a development area of about 500 square meters of development and scaling, and also offices, warehouse, and so on.
Can you describe the project you worked on with FI Group and the challenges faced?
Due to the growth that’s been taking place over the last few years, and the track record of bringing products to market, both for startups in new biological entities and in biosimilars, Europe wanted to recognise this ability of the company and has awarded us with a PERTE Salud Vanguardia.
We have been supported with the capabilities of FI to support us get this grant.
This grant is mainly intended to help us to leverage all the private investment that we’ve had and it will assist us to invest in productive equipment of the different lines that Leanbio will have in its new production plant.
What would you say the key achievements and benefits generated from this collaboration were?
At this time Leanbio is already acquiring different equipment that will be key to preparing the three production lines of the new plant.
This support will also help us to be able to hire key personnel, which will support the developments and manufacturing programs of our customers.
Right now we are aligning all these different activities so that the plant will be ready by 2025. Given the investment required in this type of production plant, specifically biopharmaceuticals, it’s always important that private money, equity, come with a share of public money, in this case it would be PERTE Salud Vanguardia. Since this implies, or links, that there is an alignment of private enterprise with public institutions.
How was your experience working with FI Group?
Working with FI Group has been very easy. Thank you, not only for your expertise in supporting companies like us, I am very pleased to be able to get this kind of support. It has also been important to be able to count on their flexibility and the different people who have been part of this project, all of them have an important technical background, and that they enabled the project to obtain this grant.
Watch the video here!
In the last few years, Open Innovation (OI) has become a well-known strategy for companies to expand their business and find a more profitable way to innovate, obtain more varied ideas and developments, relying on the union of diverse sources and experts as a way of expanding innovative potential and optimise results.
What is Open Innovation?
Open Innovation is a concept disseminated by Henry Chesbrough, which consists of creating a more participatory, distributed, and decentralised approach to innovation projects, relying on a range of companies and institutions to develop an idea, since a single company shall not have all the knowledge and resources necessary to innovate effectively on its own, regardless of its capacity or size. This absence paves the way for a search for other agents – external to the initial developer company – to contribute to the project, such as universities, startups, research institutes, and others, creating a business ecosystem.
Thus, we can consider that OI is an approach that aims to create variable collaborative business models, in which interaction between different partners is encouraged through a network of incentives. This synergy between partners results in an environment conducive to the development of innovative solutions and to create value simultaneously.
Types of Open Innovation: Inbound, Outbound, and Coupled
We can first separate open innovation methods into three types:
- Inbound: In this process, agents from outside are incorporated into the organisation. External knowledge and technology are integrated to improve company’s internal processes.
- Outbound: The organisation transfers technology and knowledge in open processes. In this case, third parties exploit internal knowledge. Furthermore, within this context, the company generates income from the sale of its private property, in a partnership system with another organisation.
- Coupled: In this scenario, Inbound and Outbound operations occur simultaneously. In this context, the company acquires external technology and at the same time transfers its ideas and technological knowledge to external corporations.
What are the benefits?
Implementing Open Innovation may seem challenging, but it doesn’t necessarily have to be: firstly, you must assess your needs; next, you will need to organise a restructuring of your company’s mindset and its current processes; finally, choose the method that best suits the innovation you have in mind.
Among the advantages of this system, we can mention:
- Reduction of risks and costs: by opening the innovation chain the organisation is sharing all project development with a third party. This allows all associated values and risks to be shared, without overburdening the company that owns the idea.
- Acceleration in the implementation of innovations: by involving external agents in project development, the tendency is for there to be an optimization of time. In these cases, the contracted third party shares its knowledge and technologies, making development processes faster and more efficient.
- Improvements to already implemented products and services: open innovation not only guarantees new products, but allows, with the acquisition of external knowledge, that products and/or services already implemented in the company are enhanced.
- Strengthening Branding: in this innovation model, the company opens its doors to the entire market. Obtaining partners contribute to publicising the business, proactively strengthening branding.
- Relevant Networking: collaboration brings together companies with the same profile and development objective as yours, in addition to integrating creative forces, talents and skills. It strengthens professional networking, creates relevant brand association within the market, and further spreads new ideas.
- Increased ROI: Return over Investment is an indicator that allows you to know how much money the company earns with each investment made. With the implementation of Open Innovation, the company tends to have a greater return on investment, as innovation is implemented quickly, cheaply, and safely promotes a chance of obtaining greater profits.
However, it is still important to remain aware of possible challenges, such as the possibility lack of clarity on objectives being pursued, lack of communication and coordination between the parties involved, selection of ideas, and intellectual property rights resulting from collaboration.
What is happening in the rest of the world?
Open Innovation is still growing. According to Economist Impact’s 2021 Open Innovation Barometer, OI’s current framework demonstrates profound progress across all sectors studied, with an average score of 62.9 (on a scale of 0 to 100, with 100 being fully open), in which large companies demonstrate greater adoption of OI Practices. As Open Innovation ecosystems advance, so does interest and implementation in the most diverse environments: also, according to this report, 95% of respondents stated that their companies practice OI, with 54% applying the practices in all or most of their projects, and 90% that have implemented key pillars of this method or plan to implement them.
In Europe, Sopra Steria’s Open Innovation Report 2023 shows a rapid uptake of OI, with almost 3 in 4 (72%) European companies conducting projects in collaboration with startups, based on around 1,648 companies and startups from 10 countries. The data also shows 89% of objectives were achieved in corporations that managed collaborations using a dedicated business unit.
The Panorama of Open Innovation in Companies in Brazil, a study released by Softex, also indicates that Open Innovation is present in 88% of Brazilian companies, considering companies of all sizes, markets, and regions of the country, having a variety of partners: 67% startups, but also including universities, companies, among other. The concept of Open Innovation is increasingly widespread in society, with the economic and competitive landscape demanding that companies implement increasingly agile and technological processes. In this way, Open Innovation process becomes a viable and good option due its opening of the innovation chain, optimisation of processes and improvement of ideas, orbiting companies, institutions, and other pillars of the market, such as universities, innovation hubs and government.
The concept of digital twins has emerged as a powerful tool across various industries in recent years, revolutionizing the way organizations design, operate, and manage complex systems.
From astronomy to smart cities, digital twins are reshaping the landscape of innovation, and driving efficiency, productivity, and sustainability.
Data-driven learning systems
Definition
A digital twin is a virtual replica or simulation of a physical asset, process, or system that enables its real-time monitoring, analysis, and optimization.
The object under study is equipped with various sensors linked to vital areas of its functionality. These sensors generate data on several aspects of the physical object’s performance. The data are then sent to a processing system and applied to the digital copy.
Once populated with the data, the digital copy can be used to run simulations, investigate performance issues and develop possible improvements, all with the aim of generating valuable information.
The 4 types of digital twin
Digital twins are divided into 4 levels, bottom-up, depending on the integration level of data and parameters:
- Level 1: Component Twin
- This represent the smallest elements of a system such as a specific part of the equipment or product.
- Level 2: Digital Product Twin
- Virtual representations of physical products or assets.
- Level 3: System Twin
- These represent entire systems or ecosystems, embracing multiple interconnected components, processes, and stakeholders.
- Level 4: Digital Process Twin
- Replicates the behaviour and dynamics of complex processes or systems, such as manufacturing processes, supply chains, or industrial operations.
Application: industrial uses of digital twins
Automotive/transportation: driving innovation with digital vehicle twins
Digital vehicle twins allow engineers to analyse how different factors such as aerodynamics, fuel efficiency, and safety features impact the overall performance. By simulating various driving conditions and scenarios, engineers can identify potential issues, refine designs, and improve the reliability and safety of vehicles.
The twins also enable predictive maintenance and condition monitoring of vehicles, enabling fleet operators to anticipate maintenance needs, minimize downtime, and optimize asset utilization.
Telecommunications: efficient networks and better customer experience
Telecommunication companies use digital network twins to create virtual replicas of their infrastructures, including towers, antennas, switches, and cables. These digital twins simulate network behaviour, traffic patterns, and performance metrics, enabling operators to identify bottlenecks, predict capacity requirements, and optimize resource allocation.
By integrating real-time data from network elements, sensors, and customer interactions, digital network twins provide operators with actionable insights into network health, enabling proactive maintenance, fault prediction, and service restoration.
Construction: building the future with BIM
In the construction industry, digital twins are known as Building Information Models (BIM). BIMs are a digital representation of a building or infrastructure project that mirror the geometry, spatial relationships, and other relevant data.
Digital twins of construction projects enable architects, engineers, and contractors to collaborate more effectively, visualize designs in 3D, and identify potential conflicts or errors before the start of construction. By simulating construction processes and sequencing activities, BIMs help to optimize project schedules, reduce costs, and improve project efficiency overall.
Medicine: personalized proactive patient care with digital health twins
Digital health twins are virtual representations of individual patients. They enable clinicians to tailor treatment plans and interventions to the patient’s unique medical history, genetic makeup, and lifestyle factors.
By analysing data from wearable devices, electronic health records (EHRs), and medical imaging, clinicians can identify trends, detect early warning signs, and intervene proactively to prevent adverse health outcomes.
Pharmaceutical companies can leverage digital twins to simulate drug interactions, predict drug efficacy, and identify patient subpopulations for targeted therapies, leading to more efficient drug discovery and development processes.
Smart cities: optimizing urban systems with citywide twins
In smart cities, digital twins are known as citywide twins. By modelling transportation networks, energy grids, water systems, and other critical infrastructure, citywide twins help to identify inefficiencies, anticipate future needs, and develop strategies for sustainable growth. They also support resilience to and preparedness for disasters by modelling the impact of natural catastrophes, pandemics, and other crises. In addition to which they also facilitate citizen engagement and participatory planning by providing interactive platforms for residents to explore urban data, provide feedback, and contribute to the development of their communities. By fostering transparency and collaboration, citywide twins empower citizens to play an active role in shaping the future of their cities.
Astronomy: exploring the cosmos with virtual observatories
Digital twins of telescopes allow astronomers to test different configurations, calibrate instruments, and optimize their performance before conducting actual observations. In addition, virtual observatories can integrate data from multiple telescopes and sensors, enabling astronomers to correlate observations and detect hidden patterns in the vastness of space.
The development of new technologies has changed our perceptions and how we grow businesses of late, bringing a range of new concepts and routines to our daily lives. Web 3.0 and metaverses, for example, are two emerging technologies that are expected to revolutionize the way we do business in the years to come, and continually scrutinized and evaluated at this point in time.
Web 3.0
Web 3.0, which may also be known as the semantic web, is a concept developed for the next generation of the world wide web, using artificial intelligence (IA) and learning algorithms as well as blockchain technologies to understand data in their sharing, and facilitate the search for information and its storage in a decentralized computer network, based on the context.
Blockchain is a method of storing information – i.e. a database – that is shared among a network of computers and duplicates and distributes transactions and information, making it difficult or impossible for the system to be manipulated and hacked.
Compared to the current internet network – referred to as Web 2.0 – a decentralized web would offer greater security and privacy, along with more data ownership, as it allows users to manage and control their personal information, rather than relying on the architecture of a central server and its relationship with the client, as is the case today.
Metaverse
“Metaverse” is a term referring to virtual worlds that allow online social interaction using digital avatars, embracing virtual reality (VR) or augmented reality (AR) technologies to create an immersive experience. Within the space created, aspects of the physical world are simulated and reinforced through resources such as social media and digital currencies, as well as avatars, events, online activity centres, etc., elements that vary from one platform to the next.
In the last two decades, the emergence and proliferation of games promoting popular metaverses, such as Minecraft and Second Life, have engendered attempts to create ever more platforms aiming to integrate virtual and physical spaces in metaverse interactions.
Technology and business
According to Citi, metaverse businesses are expected to contribute between $ 8 and $13 trillion to the global economy by 2030, with an estimated five billion users. But what is more important to start with is to consider the users likely to go for these new technologies, and what they are looking for.
In the most popular metaverses such as Roblox and Minecraft, people in general and generation Z (born between 1997 and 2010) in particular are increasingly spending their money on virtual items and accessories, many of them exclusive to the respective metaverse. Which indicates that, apart from creating virtual versions of existing physical products, there are also development potentials for unique virtual products and experiences.
Marketing can play a key role in this, too. In 2022, major brands like Disney and Nike announced strategies or projects that embraced metaverses as a new means of engaging with customers, of broadening the understanding and study of online consumer behaviour, and enabling even more personalized and precisely focused experiences tailored to the interests and needs of each target audience.
Web 3.0 could likewise enhance customer relationships. Trust-building between businesses and their customers is eased given the transparency ensured by the «immutability» of data stored in blockchain technologies, infusing the latter with greater confidence in the information’s authenticity. Better legal compliance is another benefit, with immutable transaction records that are transparent to all parties helping businesses meet governance requirements.
As Web 3.0 is designed to be decentralized, applications are unlikely to require expensive servers and data centres, and can be run on computer networks provided by end users, eliminating the need for third-party service providers. Another cost-saving benefit is the potentially easier supply chain monitoring, enabling possible issues to be identified with greater agility and better time management.
What is the upshot for us?
Web 3.0 and metaverses are highly networked in their focus on sharing content and experiences online, and both based on advanced technologies such as the AI employed in their development and blockchains, a concept undergoing constant evaluation as an integral element of Web 3.0, set to power metaverse services.
Although adjustments may be necessary, the future potential of these two technologies is huge and highly promising, offering countless opportunities for innovation in a new digital wave able to change the way we do business in all kinds of ways. Potential challenges do exist – such as the incorporation of Web 3.0 in the metaverse, potentially leading to a virtual world that is fully integrated with the internet, or the availability of resources that support these new tools – but they can be overcome with time, promising a new era of access and change.
Research and development plays a fundamental role in the advancement of science, technology and innovation. Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) countries recognize the importance of encouraging investment in R&D to boost economic growth and improve competitiveness.
In this sense, many countries have implemented a series of tax incentives to promote investment in R&D. These incentives seek to reduce the costs (and cover the risk) associated with research and development, encourage collaboration between companies and research centers, and stimulate the creation of highly qualified jobs in the private sector.
Tax incentives for R&D
One of the most common incentives is the tax deduction for R&D activities. This scheme allows companies to deduct a percentage of R&D expenses from their tax base, which reduces the tax burden and increases the resources available for investment in research and development. Some countries offer additional deductions for the hiring of qualified personnel or for the acquisition of technological equipment.
Another incentive used in many OECD countries is the R&D tax credit. This mechanism allows companies to obtain a tax credit equivalent to a percentage of R&D expenses. Tax credit is a direct benefit that individuals can use to reduce the tax payable or even obtain a cash refund if the credit exceeds the tax owed, unlike tax deduction.
In addition to direct tax incentives, some OECD countries have implemented special regimes for research and development, which offer additional benefits, such as exemption from taxes on income derived from the exploitation of patents or reduction of taxes on profits from patents. capital obtained from the sale of assets related to R&D.
In many cases, R&D tax incentives are designed to encourage collaboration between companies and research centers. For example, some countries allow the transfer of R&D tax credits between companies, facilitating collaboration on joint research projects. Other incentives include the possibility of deducting R&D expenses carried out by third parties, such as universities or research centers, as long as effective collaboration is established.
R&D Tax Incentives Intensity Map
It is important to highlight that tax incentives for R&D vary significantly between different countries. Each country has its own regulatory framework and establishes its own conditions and requirements to access tax benefits. Some countries offer more generous incentives, while others have stricter requirements. Therefore, it is essential that companies interested in taking advantage of these incentives consult the current legislation in each country and obtain appropriate advice.
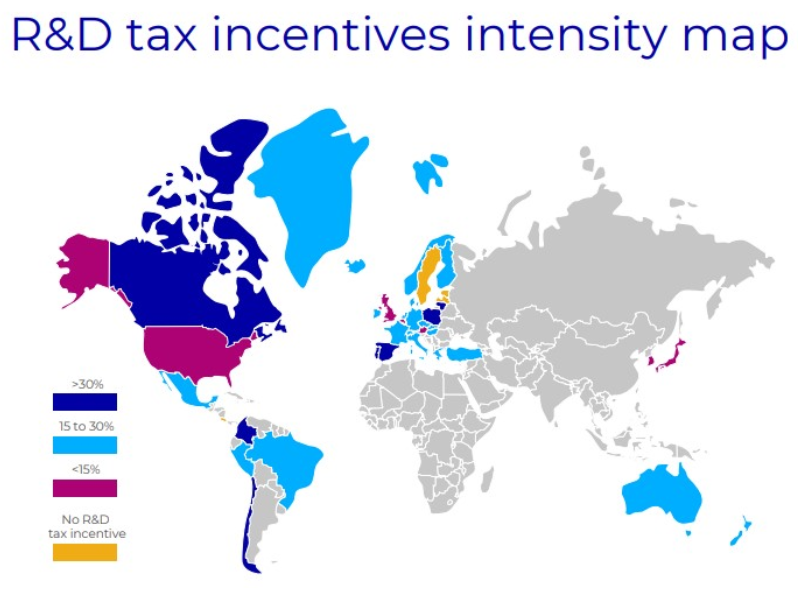
For this map to be representative of the different nature of R&D tax incentives (volume- based and incremental tax credits, super deduction), we took the scenario of a large company with R&D expenses during the last 10 years. Every year the amount of eligible R&D expenses is growing, as such, the claimant can apply for incremental R&D tax credits and deductions. The effective return on the R&D expenses is shown in the legend as a percentage of posttax reduction.
How can FI Group help you?
At FI Group we have extensive knowledge and experience in obtaining these tax incentives on different continents, with a global and coordinated strategy that is also complemented by the management and obtaining of public aid and subsidies for different types of investments. The combination of both incentives, from a strategic point of view and from a financial point of view, can mean for the company an important differentiation and competitive advantage within its scope of action.
FI Group has over 20 years of experience. Our specialized experts are at your disposal to analyze the fit of your project and advise you on obtaining tax incentives. Contact us.
What is the Digital Transformation?
The digital transformation is not just one thing or activity, but an entire process by which companies enhance the digital technology in their businesses, using it to change or create new processes, cultures, and customer experiences, optimising all the activities right from the start. The process can vary from one company to the next, depending on how the technology is applied and implemented.
Many ways lead to digital transformation and its changes, and every organisation’s journey will be unique. A company might add AI as a tool for optimising the customer experience or for developing new strategies to make its daily team routines more efficient. The organisation’s operations are rewired by the constant evolution and integration of technologies that improve its functions.
To be successful, the digital transformation calls for a variety of coordinated activities: it is a long-term effort with continuous adaptations and changes.
Defining Digital Transformation Strategies
- Transformation business strategy: The technological route you opt for now will decide your company’s success.
- Realigning business operations: What do your customers and employees need most, and how can digital processes help? The design of better processes can be based on these questions.
- Adoption of new practices for agility and experimentation: As customer expectations mount and the pace of change quickens, new ways of working need to be introduced. To be successful, the digital transformation needs to pursue a varied approach that pays heed to the availability of technologies and human adaptability.
- Flexible core technologies for sustainable change: By staying flexible, you can catalyse innovation across your enterprise and form ecosystem partnerships more easily to drive speed and scale. It is important not to get stuck with just one technology. Openness to new possibilities and improvements allows for fast and sustainable changes, while keeping the needs of your client or team in focus is key.
- People management: How can technologies enable better knowledge sharing and collaboration? What should the future of work look like? Technologies face workers with new challenges, but can also solve many of them. To make them work, the digital basis, digital operations and digital skills of the workforce all need to be supported by the management and a culture that welcomes new technologies and seeks the best ways of integrating them in everyday life.
Digitalisation vs. Digital Transformation
Even if the mention of digital transformation will automatically make you think of digitalisation, it is important to emphasise that the two are not the same. Digitalisation can be seen as an integral part of the digital transformation process and one of its ultimate pillars. But what is important even before this point is to first identify the requirements and possible improvements between teams and customers and their systems, and then set up a process for changing the culture and adapting routines to the new system installed.
Digitalisation is mostly about technologies – their application to change a business and automate business processes, step by step or rolled-out as a project – whereas the digital transformation is not, but can include digitalisation as an integral part in its continuing quest for new procedures while paying greater attention to people and their attitude to changes in the company culture.
What does the digital transformation mean for FI Group?
In FI Group, too, the digital transformation is brought about in the most diverse ways, all aimed at providing added value for clients and employees. The digital transformation here proceeds incrementally in a stream-aligned structure – a model of organisation and team interaction where squads with digitalisation strategies for services in various areas globally develop and manage digital tools for teams and clients.
Applying new ways of systematising documents and data is meanwhile another operative element of the digital transformation – the establishment of new organisational methods facilitates and speeds up the work and access to required information.
More locally, we also have our Scientific Department, established by FI Group France in 2019, which leads the research relating to artificial intelligence and NPCs, aiming to enable a regular scientific and technological supervision for proposing new approaches and supporting R&D Financing Consultants in their daily missions.
OpenAI, Chat GPT, and generative language models
2023 will go down as the breakthrough year for ChatGPT due to the intuitive capabilities and wide scope of applications of the tool.
But where did it all start?
Created in 2015, OpenAI has notable founders such as Elon Musk and Sam Altman with the aim of integrating artificial intelligence into society for the benefit of humanity. Looking back on the last seven months, you can definitely say their work has impacted society through their creation of ChatGPT.
In a nutshell, ChatGPT is an AI application that has been ‘trained’ to understand natural language and conversation. Pulling data from the internet and presenting its findings in easy to understand responses. Furthermore, it can be used as a translator, create content, summarise text and process / write code.
The R&D
Ironically, you can find out about the R&D behind ChatGPT by simply asking it. The tool identifies five components that make up its development:
- Training Data – Large amounts of text, sources that include books, articles, and websites – where it can capture grammar and context.
- Pre-Training – Learning to predict the next word in sentences and understand the patterns and relationships it sees from its training data.
- Fine-tuning – Final stages of learning translation, question answering, and conversation.
- Architecture and Algorithms – Transformer models help natural language processing tasks, for example, capture contextual relationships effectively.
- Iterative Development – The final stage of testing the previous four components, making fine adjustments to any imperfections.
However, it can be difficult to put all this development into perspective and understand the gravity of its intelligence. The English language is comprised of one million words. In comparison, ChatGPT is made up of ten billion words, including fifteen languages (incl. English, French, Russian, Chinese, Arabic and Urdu), and sixteen programming languages (incl. Python, Java, JavaScript, C++ and, HTML/CSS).
If you wanted to dive deeper into the development of the tool, tokenization is the breaking down of the sequence of text into smaller units, appropriately called tokens. These help ChatGPT’s natural language processing (NLP) for further development.
Applications
As previously mentioned, OpenAI reached their goal of impacting society through their work. The applications for ChatGPT are vast, content creation, consultancy, and customer support to name a few.
A popular term being used more and more within industries is, ‘ChatGPT won’t take people’s jobs, people that use it will’. Which to an extent is correct. If utilised correctly by competent professionals with in-depth knowledge of their profession, then ChatGPT can allow for streamlined workflows and increased productivity.
Despite having ten billion words, mistakes can still be made. Users who copy and paste its responses risk not only incorporating the errors the tool might have created but also limiting themselves by hindering personal development in their respective careers.
Introducing MarIA
FI Group has made the decision to move away from ChatGPT. At a glance this decision might undermine what was said previously about streamlining workflows, however, we have opted to use a different tool. We are launching MarIA which uses AzureGPT functions. Similar to ChatGPT, but can ensure that conversations and data shared with it remain in the Azure environment which provides an additional level of security.
On the topic of ChatGPT, FI Group France Scientific Director Charlie Grosman said:
‘while it generates useful and relevant information, in a short period of time, it is not a technology that employees should trust at an exact level».
What does MarIA mean for our clients?
FI Group requires a lot of sensitive information from our clients such as confidential R&D project details and employee salary, if this information is shared with ChatGPT it is then stored in OpenAI’s database and outside of our control. MarIA ensures that any private information is kept safe in our own database and cannot be accessed by anyone outside of FI Group.
Moreover, MarIA will also limit how much FI Group employees can use its functions. Ensuring that work is being done by real people and aided by the tool, when necessary, rather than the other way round. Meaning, clients can be assured they are getting genuine expert client opinions.
Given the great volumes of data and information to be handled these days, companies need to implement security measures and processes to guarantee data protection and privacy.
In the IT world, companies are becoming increasingly vulnerable to possible cyberattacks. It is therefore crucial for all organizations to have information security systems enabling them to analyse and detect possible anomalies that could indicate a potential threat to their servers.
Which is why we at the FI Group have an information security management system (ISMS) to guarantee the confidentiality and protection of internal information and our clients’ data. And in this respect, we have also been awarded the ISO 27001 certification again.
This certification demonstrates our commitment to providing high-quality products/services while adhering to strict international standards. We’re proud to have achieved its renewal, which recognizes the quality and strength of the FI Group’s ISMS.
Why ISO?
Information security management systems are made up of policies, organizational structures, procedures, processes and resources necessary to guarantee the confidentiality, integrity and availability of information in an organization.
For some years now, leading international standardization bodies have been establishing requirements for the implementation of information security management systems. One of the most frequently used among them is the 27001:2017 standard by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) because it is widely recognized internationally and permits implemented information security management systems to be certified.
Advantages of being (ISO) certified
- The certification helps us to differentiate ourselves from competitors by highlighting our extensive commitment to information security and data privacy, along with defining high quality and excellence standards.
- It demonstrates that we have a powerful information security and privacy management system in place that complies with national legislations.
- The certificate and underlying ISMS make us more competitive by reducing costs that would have an impact on our business continuity.
- Our processes become safer, as well as more traceable.
- And it efficiently tests our compliance with the security requirements of third parties.
Which countries is the FI Group ISO 27001 certified in?
We have implemented security measures and processes in several FI Group countries to ensure that all our systems are safe, and to demonstrate our commitment to customers. The countries already certified are:
– Belgium
– Brazil
– Canada
– Chile
– Colombia
– France
– Portugal
– Spain
– USA
– United Kingdom
To be included in the certification this year:
– Germany
– Italy
Spain additionally has an ISO 27701certificate demonstrating an even higher level of privacy and data protection.
How does the renewal process work?
The renewal process has two major parts and takes a whole year.
The first part is an internal audit where all the ISO domains are evaluated, and we can verify the strength of the controls implemented in the company.
Once the internal audit has been completed, we focus on the aspects identified as potential improvement areas while working on the continuous development of our information security management system.
This process takes a whole year because it needs to continuously update and develop the implemented controls while adding new checks and processes that help to strengthen our company.
The second major part in October is the external audit where the company’s compliance with the controls and domains required by ISO 27001 is evaluated.
Once this audit is done, the country in question will either be certified again, unless of course it has failed to pass it.
Before and after certification
We can see an improvement in our company’s processes and safer procedures that allow us to work with our own and customer information while maintaining the highest security standards.
The difference after implementing the certification is most tangible in our company’s day-to-day business and the confidence that we are working with truly private and confidential data.
Innovation and technological development lie at the core of FI Group’s DNA, filtering down through every member of the group. These elements are deemed indispensable for fostering growth and bolstering the competitiveness of any country.
This stemmed from the aftermath of the Covid-19 pandemic. Where both national and international policies strategically pivoted towards promoting investment in R&D&I and energy efficiency to reignite various sector’s work after the pandemic.
Regional, national, and European grants emerged as the primary public tools to drive economic revitalisation and foster growth across continents. Adequate public funding plays a pivotal role in facilitating the execution of large-scale R&D projects, which are critical for addressing the challenges posed by the prevailing political and economic landscape. These grants not only present opportunities for entities to confront these challenges but also serve as catalysts, inspiring innovation, differentiation, and investment to ensure development.
Currently, the continent boasts over 100,000 funding opportunities, encompassing regional, national, and European grants. Recognising the significance of these public funding opportunities, we have assembled a panel of experts from different countries to engage in a comprehensive discussion on the subject.
Among those attending this round table were:

1. First question: How many calls are there in each of your countries?
«Just imagine, according to the Spanish national database, in 2022 there were 62,817 calls for proposals,» –AV.
«At the regional level alone in this 2023, 459 calls have already been opened» –NZ.
«And we are only in May, we still have more than half the year ahead of us»- FAC to which Roberta explains that in Italy right now there are more than 650 published and waiting for the publication of another 97.
2. What do the calls for proposals mean for the different companies?
«I think we all agree that these calls for proposals, at all levels and for all types of companies, mean the possibility of making an investment or starting a project that would otherwise be difficult to carry out,» –VO.
«I totally agree. In addition to the fact that it makes it possible to grow the business and expand into new markets, and even to become known as a key player in the different sectors, especially in R&D calls,» –RD
«We cannot forget that it has an incentive effect, and that it also makes it possible to achieve results in a shorter period of time than would be possible without these calls». – AV
3. What role does FI Group play in the achievement of these objectives? How can we accompany the different companies in these processes of application to the different calls?
«At the level of the processes of fitting into the calls, application, monitoring and justification; for a company it is a tremendously bureaucratic and complex process. Being able to count on a trusted partner with years of experience is essential,» –AV *while her colleagues nod in agreement.
«With the support of a specialised agent or one that is close to the convening agency is a «privilege» that few actors have in this ecosystem. FI Group has a long experience and great success in all the stages that my colleague explained earlier,» -FAC
«We have teams of experts in both technical and financial areas, without forgetting that we are part of the ecosystem and know all the parties involved, being active and proactive in creating value propositions to improve the systems and funds so that they are more attractive and competitive,» –MO
«We also help to involve one or more stakeholders in relation to the sector or area, and we help and accompany them to improve collaboration. This is precisely due to a large global database of contacts that we have been working on during the 20 years of FI Group’s existence, which allows us to support our clients in an aggregated way, both at multi-country, multi-sector and multi-service levels».-RD
«Absolutely. To a great extent to the experience acquired, the knowledge, the connection networks, we have the capacity to offer this multi-country, multi-sector and multi-service service, but we also continue to do it as the first day, with an individual team per client, with an exclusive and close accompaniment, always making their project ours» –NZ
4. What are the most strategic sectors right now?
«I think we all agree that currently the most strategic sectors, not only for FI Group but for the whole of Europe and therefore for our clients, are industry in general and specifically all the electro-intensive ones, as well as everything related to energy, decarbonisation and hydrogen,» –NZ
«Automotive, ICT, Tourism, biotechnology, textile, chemical…». – MO
«From FI Group we continue and will continue to accompany all companies in achieving their objectives and their R&D&i projects, solving their doubts, finding the best fit in consortia or accompanying them in the justifications of the calls they have already achieved. This is and will be the driving force of all the colleagues who are part of this company». –VO
Hit the links below to access their LinkedIn profiles:
What is Articifial Intelligence (AI) ?
Articifial Intelligence is a technology that belongs to the field of computer science and aims to create systems and algorithms that run in a dynamic environment, based on the collection and processing of data. These computer programs must be able to simulate human intelligence. The main objective of AI is to create intelligent machines that can help solve complex problems in many fields.
There are several categories of Articifial Intelligence (AI), which can be classified according to their capability and level of sophistication. Here are some of the most common categories of Artificial Intelligence :
- Weak Articifial Intelligence : This category of AI can perform specific and limited tasks. It is often used for applications such as speech recognition or image classification. While it is very effective at specific tasks, it can’t replicate the versatility of human intelligence.
- Strong Articifial Intelligence : This category of AI is designed to replicate human intelligence in its entirety. It can think autonomously, solve complex problems, and perform a wide variety of tasks without being explicitly programmed for each one. However, strong AI does not yet exist in its entire form and scientists continue to work on ways to develop it.
- Super Articifial Intelligence : This category is a hypothetical version of AI that would be capable of surpassing human intellectual abilities in all areas. This form of AI does not yet exist, but some AI experts predict that it could be developed in the future.
To get as close as possible to human behaviour, Articifial Intelligence needs a lot of data, as well as a processing and learning capacity. To achieve this, three components are needed:
- Computer systems,
- Data with management systems (they can be collected from databases, files, etc.),
- Algorithms. Once the data has been processed, a machine learning model can be trained using algorithms. This model is then trained to learn to perform a specific task from the data autonomously.
To enable computers to learn from data, Articifial Intelligence relies on Machine Learning models (a method that aims to teach machines to learn from data and improve with experience). There are 3 learning methods used:
- Supervised: which uses defined data to learn to identify patterns and make predictions,
- Unsupervised: which learns from undefined data. It uses techniques such as clustering or dimension reduction to identify patterns and relationships in the data,
- Semi-supervised: uses both defined and undefined data.
It is important to note that AI is a constantly evolving field of research, and that definitions and distinctions between different types of Artificial Intelligence may change.
What is Articifial Intelligence used for?
The main goal of AI is to create intelligent machines that can help solve complex problems in many fields, such as medicine, engineering, finance, security, social sciences, gaming, etc. Articifial Intelligence is seen as a key technology for the future and has the potential to transform the way we live and work.
These examples are just a small portion of the application areas for AI, and new uses are regularly discovered as the technology continues to advance. AI can therefore be used to improve efficiency, accuracy, safety, and quality in many different areas.
The example of ChatGPT
One of the most popular supervised AI at the moment is Chat GPT (Chat Generative Pre-trained Transformer). This conversational tool aims to help its users solve problems, answer questions, and provide information in various domains. It therefore generates text from input data (questions, queries, etc.). It is based on Natural Language Processing technology (NLP) and uses unsupervised learning. It has been trained on a very large corpus of text to learn how to generate consistent and relevant answers based on user queries. This is possible because it has access to huge amounts of text, from various sources.
FI Group Scientific Department
As a pure player in the R&D ecosystem, FI Group France has created a Scientific Department back in 2019. They lead research in Artificial Intelligence and NLP mostly. This department is composed of seven Researchers (including two Industrial PhD CIFRE). One PhD student is conducting a thesis on data extraction and the construction of algorithms to evolve their grouping by theme and subject. The second PhD student is doing a thesis on unsupervised learning on data flows. She is developing methods capable of clustering data continuously.
The objective of this department is to allow the realization of a regular scientific and technological watch to propose new approaches, and thus to support R&D Financing Consultants in their daily missions.
These projects are possible thanks to the development and experimentation of techniques in Machine Learning and Automatic Language Processing. These processes facilitate the search for information in a large volume of data. A third research topic concerns the acquisition of new knowledge and the involvement of collaborators, via Gamification processes and serious games.
The NASA project
One of the projects supported by FI Group is called NASA. This AI makes it possible to search for scientific articles based on various concepts.
For each query, the articles published between 2019 and 2021 (about 13 million) are used to represent this knowledge in the form of a graph of concepts. It is then possible to display 10 scientific articles published for each concept.
The first prototype of NASA «First STEP» (Scientific Taxonomy Exploration Prototype) was launched in March 2022. The second and the third were respectively put online in September 2022 and February 2023. This «Third STEP» proposes improvements in performance, quality and user experience.
Why does digital transformation matter?
Case studies have argued that 50% of employees could be replaced by machines because of the big technological advancements in AI in the era of Digital Transformation, however, we see this as a complement instead as a negative human replacement.
We see computer software’s and AI as an addition to our activities, working alongside people who are part of the chain of vision. People can improvise, be reactive and think critically, showcasing the advantage of people in unexpected situations. There is a clear link between the collaborative work that can be done by AI and people, rather than a separation.
Knowing how to be an efficient and productive team is always the main aim of any successful partnership. As discussed, both people and AI have different strengths and weaknesses. By delegating tasks based on these strengths and weaknesses the digital transformation and partnership between people and AI can become more efficient and impactful.
What role does consultancy play in digital transformation?
It is becoming harder and harder to talk about Consultancy without mentioning digitisation. The digitisation of consultant tasks can be eased by Robotic Process Automation (RPA) software’s. These systems are designed to emulate human’s actions when interacting with digital systems, such as recognising and extracting relevant data.
This automation undoubtedly contributes to the streamlining of the consulting process. It can gather information immediately, transfer documents instantly, create news queries in a few minutes, solve the incidences quickly and in the stages of verifying or making changes to procedures.
So, the digital transformation allows for flexibility within automation systems, which develops ease and efficiently, making the consultants project writing time shorter. This is also a benefit for the client as it allows for quicker turn around time on R&D reports.
Focusing on the improvement of the value add of our services has always been one of our greatest priorities. Innovation and technology are core pillars of our business, we are always looking for ways to improve our internal procedures through digital advancements that are being made, to provide the best and most efficient results for our clients.
The FI Group solution
- How can FI Group help our clients in this era of digital transformation?
We offer a free audit to highlight and show our clients areas in their R&D process that can be improved by our team and service.
To improve this process, we have created an application that have improved the line of communication between FI Group and clients, and allows 24h access to updated claim information, improving our traditional services through new digital tools.
Introducing FI Connect. A new digital space that integrates several applications on a single platform. Benefiting our customers by providing greater transparency and showcasing the digital transformation that FI Group is currently undergoing and that will drive productivity for clients and consultants alike.
Welcome to FI Connect
Find out if the service is available in your country to book a demo:



