automation
FI Group Expertise
Artificial intelligence has never been more integrated into daily life and business world. Since the launch of ChatGPT in 2023, the number of companies adopting AI has jumped by 20%, reaching 78% of all organisations questioned in the «State of AI: Global Survey» by McKinsey & Company.
Clearly, AI is no longer just an optional tool; it’s becoming an essential strategic asset for companies aiming to stay competitive and innovative. But as businesses invest efforts into AI, they also face a subtle but significant risk: cognitive debt. According to recent MIT research (2025), overreliance on AI can erode essential human skills like creativity and critical thinking.
So how can companies harness the power of AI without compromising their greatest resource: their people?
Accelerating Innovation with AI
AI is often associated with boosting operational efficiency, but its potential goes far beyond that. It can significantly accelerate innovation across every stage of the R&D process, from generating ideas and prototyping to testing and launching new products.
Traditionally, innovation was slow, costly, and limited by human resources and physical experimentation. Now, AI lets companies rapidly run thousands of simulations and test numerous hypotheses at once, tasks that used to take months or years can now be completed in days or even hours.
For instance, pharmaceutical giants like AstraZeneca have partnered with AI startups such as BenevolentAI to quickly screen millions of chemical compounds. This collaboration has dramatically shortened the drug discovery timeline, bringing new treatments to market much faster. AI’s ability to analyse huge datasets and detect meaningful patterns also improves decision-making, ensuring companies invest their R&D budgets wisely.
According to Gartner (2024), companies that integrate AI-driven analytics into their research can more accurately predict market trends, customer preferences, and technological feasibility. Brands like Unilever and Procter & Gamble use AI analytics to better anticipate consumer trends, aligning their innovation strategies closely with market demands.
The Hidden Risk: Cognitive Debt
Despite its undeniable advantages, AI also presents hidden risks.
A recent MIT study, «Your Brain on ChatGPT» (Kosmyna et al., 2025), highlighted that excessive reliance on AI can reduce brain activity linked to creativity, critical thinking, and memory. Participants who regularly depended on AI exhibited weaker cognitive engagement and poorer recall compared to those who completed tasks without AI. This phenomenon, known as «cognitive debt», occurs when individuals consistently outsource mental tasks to technology, gradually weakening their own cognitive abilities. Though AI streamlines workflows, excessive reliance can unintentionally undermine the very human qualities that drive sustained innovation.
Balancing AI and Human Potential: Practical Strategies
To fully realize AI’s benefits while avoiding cognitive debt, businesses should consider these best practices:
- Complementary use of AI: Encourage teams to see AI as an enhancer of human capabilities rather than a substitute.
- Continuous learning: Invest in training programs that simultaneously develop critical thinking, creativity, and technological proficiency.
- AI Governance: Create clear guidelines on ethical AI use, transparency, and human oversight, as recommended by authorities such as McKinsey and Harvard Business Review (2024).
By implementing these strategies, businesses can leverage AI effectively while preserving and enhancing their human capital.
Navigating the AI Revolution Thoughtfully
AI presents tremendous opportunities for accelerating innovation, increasing efficiency, and creating lasting competitive advantages. Yet, as businesses embrace AI, maintaining awareness of cognitive risks remains crucial. The smartest path forward involves strategically balancing AI’s powerful capabilities with the irreplaceable creativity and ingenuity of human talent.
Companies that master this balance will lead the future, strategically integrating AI to unlock sustained innovation and growth.
Did you know that over 70% of companies worldwide are already using some form of artificial intelligence in their processes? Currently, AI is not only transforming industries but also changing the way teams work and add value.
At FI Group, we have made artificial intelligence an ally to enhance our internal capabilities, improve our efficiency, and deliver better results for our clients.
The integration of AI into our daily work allows us to:
- Automate routine tasks: Automation through AI can save up to 30% of time on administrative and management activities
- Prioritize what really matters: By letting AI handle low-value tasks, our team can focus on strategic and creative projects that generate real impact for our clients.
- Quickly access and process key information: With the help of MarIA, our integrated artificial intelligence tool, we can analyze large volumes of documents and access cross-sectional information about our clients and the company to process and obtain relevant information in minutes.
- Improve decision-making: A recent IBM study reveals that 42% of consulting firms already use AI to support decision-making and real-time data analysis
How We Use AI at FI Group
The implementation of AI at FI Group spans several key areas that have transformed our daily operations:
- Support for teams: Tools like MarIA, SmartRead, and Copilot interact with each employee, assisting in document management and answering operational questions. This facilitates a review of the state of the art with an academic database, allowing human talent to focus on developing high-value information for the process.
- Process automation: The digitization of tax documentation has become a quick and efficient task thanks to tools like the invoice scanner, which uses locally trained AI. This not only speeds up document analysis but also improves efficiency in responding to our clients.
- Continuous learning: AI is not static; it learns from our processes and provides teams with personalized suggestions, helping to improve every day. This cycle of continuous learning is essential for adapting to the changing needs of the market and our clients.
For the successful integration of AI, it is essential to consider several aspects:
- Organizational culture: We are committed to the ongoing training and updating of our team. Training focuses not only on the use of tools but also on understanding how AI can enhance our capabilities.
- Ethics and responsibility: At FI Group, we ensure the safe and ethical use of data, protecting the confidentiality of our clients’ information. Trust is a fundamental pillar in our relationship with them.
- Long-term vision: We see AI as a tool to enhance human value, not to replace it. Our focus is on how artificial intelligence can complement and improve human work, creating synergies that benefit both our employees and our clients.
Artificial intelligence is a fundamental part of our operational strategy. It allows us to be more agile, respond better to our clients’ needs, and find new ways to deliver real value in a competitive environment. Our experience shows that when AI is integrated with a human and orderly vision, the results multiply.
In a world where innovation is the key to surviving and thriving, artificial intelligence is not just a tool but a strategic partner. By adopting AI responsibly and ethically, we not only optimize our processes but also open the doors to a future full of possibilities. Companies that dare to integrate AI into their DNA not only stay at the forefront of innovation but also become leaders in their respective sectors, creating a lasting impact on society and the economy.
The AI-driven transformation is a continuous journey. At FI Group, we are committed to continuing to explore new applications and improvements in our artificial intelligence tools, ensuring that every day we can provide an even more efficient and valuable service to our clients. Artificial intelligence is the path to a brighter and more productive future, and we are excited to be part of this revolution.
Lorem Ipsum is simply dummy text of the printing and typesetting industry. Lorem Ipsum has been the industry’s standard dummy text ever since the 1500s, when an unknown printer took a galley of type and scrambled it to make a type specimen book. It has survived not only five centuries, but also the leap into electronic typesetting, remaining essentially unchanged. It was popularised in the 1960s with the release of Letraset sheets containing Lorem Ipsum passages, and more recently with desktop publishing software like Aldus PageMaker including versions of Lorem Ipsum.
Funding Investments
Lorem Ipsum is simply dummy text of the printing and typesetting industry. Lorem Ipsum has been the industry’s standard dummy text ever since the 1500s, when an unknown printer took a galley of type and scrambled it to make a type specimen book. It has survived not only five centuries, but also the leap into electronic typesetting, remaining essentially unchanged. It was popularised in the 1960s with the release of Letraset sheets containing Lorem Ipsum passages, and more recently with desktop publishing software like Aldus PageMaker including versions of Lorem Ipsum.
Why do we use it?
It is a long established fact that a reader will be distracted by the readable content of a page when looking at its layout. The point of using Lorem Ipsum is that it has a more-or-less normal distribution of letters, as opposed to using ‘Content here, content here’, making it look like readable English. Many desktop publishing packages and web page editors now use Lorem Ipsum as their default model text, and a search for ‘lorem ipsum’ will uncover many web sites still in their infancy. Various versions have evolved over the years, sometimes by accident, sometimes on purpose (injected humour and the like).
Where does it come from?
Contrary to popular belief, Lorem Ipsum is not simply random text. It has roots in a piece of classical Latin literature from 45 BC, making it over 2000 years old. Richard McClintock, a Latin professor at Hampden-Sydney College in Virginia, looked up one of the more obscure Latin words, consectetur. Salvatore
Lorem Ipsum is simply dummy text of the printing and typesetting industry. Lorem Ipsum has been the industry’s standard dummy text ever since the 1500s, when an unknown printer took a galley of type and scrambled it to make a type specimen book. It has survived not only five centuries, but also the leap into electronic typesetting, remaining essentially unchanged. It was popularised in the 1960s with the release of Letraset sheets containing Lorem Ipsum passages, and more recently with desktop publishing software like Aldus PageMaker including versions of Lorem Ipsum.
Why do we use it?
It is a long established fact that a reader will be distracted by the readable content of a page when looking at its layout. The point of using Lorem Ipsum is that it has a more-or-less normal distribution of letters, as opposed to using ‘Content here, content here’, making it look like readable English. Many desktop publishing packages and web page editors now use Lorem Ipsum as their default model text, and a search for ‘lorem ipsum’ will uncover many web sites still in their infancy. Various versions have evolved over the years, sometimes by accident, sometimes on purpose (injected humour and the like).
Where does it come from?
Contrary to popular belief, Lorem Ipsum is not simply random text. It has roots in a piece of classical Latin literature from 45 BC, making it over 2000 years old. Richard McClintock, a Latin professor at Hampden-Sydney College in Virginia, looked up one of the more obscure Latin words, consectetur. Salvatore
FI Group weighs the benefits and challenges of business automation
Automation driven by technological advances such as artificial intelligence, robotics and machine learning is rapidly changing the landscape of work. Repetitive and manual tasks previously performed by humans are being automated, freeing up time and resources for more creative, strategic, and complex activities.
Automation is guaranteed to boost the productivity, efficiency and safety, along with reducing costs and human error. It is essential to recognise, however, that this new reality also entails some adversities including rising unemployment, social inequality, and a need to retrain the workforce. To reflect on this need to adapt and develop new skills is essential if a business is to thrive in an increasingly automated world.
What is Business Automation?
Business automation is the current use of computerised systems, software applications, devices and other technological tools to perform processes automatically or semi-automatically, entirely without or with minimal human intervention. It can de facto be applied to various levels and areas of the company, from operational to managerial processes.
As the technological advances and automation tools themselves are increasingly becoming accessible to people unable to program them, business automation is found ever more frequently in all company routines. Especially so in the routines of companies aiming for continued competitiveness by banking on innovation.
Benefits and Challenges of Business Automation: The Benefits
By the strategic implementation of innovative technologies, business automation can offer a range of benefits that optimise the performance and open up a range of growth potentials.
Greater Productivity, Efficiency and Quality
Automation saves time, reduces effort, and the incidence of manual errors. Automated processes guarantee consistent results and a high quality, with tasks carried out identically and without human error. And if there should be errors nonetheless, they can all be corrected by changing the underlying process.
Reducing Costs and Optimising Resources
By eliminating redundant tasks, automation can optimise the use of resources, significantly reducing the company’s operating costs, along with the waste of materials, time and energy.
More Employee and Customer Satisfaction
Wherever manual tasks are «tedious» or very demanding, automation enables staff to turn to more pleasurable and creative activities, boosting their satisfaction. And by dedicating themselves to activities that please them more, they end up having more time to focus on better customer service.
Greater Competitiveness and Strategic Advantages
In an increasingly competitive market, automation puts a company at the forefront of innovation, providing a crucial strategic advantage for success. By automating specific processes, you will be able to respond to market changes and customer needs with the flexibility that entails. Freeing up resources will meanwhile also help you make the most of new market opportunities.
Key Business Automation Processes
When weighing up the benefits and challenges of business automation, it is imperative that business automation not be viewed in an exclusive manner, as there are various automation technologies that organisations can apply.
Business process automation (BPA) is a strategy pursued to optimise a company’s processes by implementing software and technologies. As a rule, BPA involves creating automatically sequenced activities that respond to process flows and not just individual tasks. Various software programs are available to automate the management and provision of financial reports, HR processes, marketing activities, the commercial management, and even workflows, to name but a few.
Robotic process automation (RPA) uses software «bots» to imitate human responses at the user interface, automating recurring and rule-based tasks. This in turn permits problems to be solved without interrupting human workflows or the need for human monitoring and supervision, unlike other automation methods.
RPA supports companies in activities such as processing requests, sending notifications, updating profiles, making complex calculations, monitoring already automated tasks, and many others. Call centres, data migration, help desks and credit applications are only four examples where RPA can be useful.
Finally, intelligent process automation (IPA) is a technology resulting from the convergence of robotic process automation (RPA) and various AI technologies in the automation of business processes. IPA aims to take automation to a higher level of complexity, increasing agility across the board. Some examples of IPA include new, intelligent CRM systems that eliminate manual tasks, inventory control with the ability to automate an organisation’s entire value chain, or quality management.
Benefits and Challenges of Business Automation: The Challenges
According to a report by the McKinsey Global Institute, automation could eliminate 15 % of all global working hours by 2030, leaving around 400 million people unemployed.
Among the countries this report takes a closer look at, it is estimated that workers in Japan will be the most affected by this development. But the story is similar in the United States, where 23 % of all working hours could be lost to services and automation processes, taking millions of jobs along with them. [Jobs threatened by automation | source: Statista]
Medium-term automation could lead to the loss of 39 million jobs in the US by 2030, while rapid automation could make 73 million people lose theirs. But to offset the potential job losses, around 20 million of these newly unemployed could transfer to similar jobs where they perform slightly different tasks.
Even so, a significant proportion would need to be fully retrained in the US and many other developed countries. According to McKinsey, a third of the US workforce may have to be retrained by 2030, as well as almost half the Japanese workforce.
Rapid automation could also cost China and India 236 and 120 million jobs, respectively. The worst-case scenario in Japan would lose 30 million jobs. Mexico could have 18 million workers made redundant by then, and Germany 17 million.
The jobs most at risk from automation tend to be physical and predictable, such as fast food workers or machine operators. The safest jobs are generally the less predictable ones, including managers, engineers, scientists, teachers, and plumbers. [Automation could eliminate 73 million jobs in the US by 2030 | source: Statista]
In the last few years, Open Innovation (OI) has become a well-known strategy for companies to expand their business and find a more profitable way to innovate, obtain more varied ideas and developments, relying on the union of diverse sources and experts as a way of expanding innovative potential and optimise results.
What is Open Innovation?
Open Innovation is a concept disseminated by Henry Chesbrough, which consists of creating a more participatory, distributed, and decentralised approach to innovation projects, relying on a range of companies and institutions to develop an idea, since a single company shall not have all the knowledge and resources necessary to innovate effectively on its own, regardless of its capacity or size. This absence paves the way for a search for other agents – external to the initial developer company – to contribute to the project, such as universities, startups, research institutes, and others, creating a business ecosystem.
Thus, we can consider that OI is an approach that aims to create variable collaborative business models, in which interaction between different partners is encouraged through a network of incentives. This synergy between partners results in an environment conducive to the development of innovative solutions and to create value simultaneously.
Types of Open Innovation: Inbound, Outbound, and Coupled
We can first separate open innovation methods into three types:
- Inbound: In this process, agents from outside are incorporated into the organisation. External knowledge and technology are integrated to improve company’s internal processes.
- Outbound: The organisation transfers technology and knowledge in open processes. In this case, third parties exploit internal knowledge. Furthermore, within this context, the company generates income from the sale of its private property, in a partnership system with another organisation.
- Coupled: In this scenario, Inbound and Outbound operations occur simultaneously. In this context, the company acquires external technology and at the same time transfers its ideas and technological knowledge to external corporations.
What are the benefits?
Implementing Open Innovation may seem challenging, but it doesn’t necessarily have to be: firstly, you must assess your needs; next, you will need to organise a restructuring of your company’s mindset and its current processes; finally, choose the method that best suits the innovation you have in mind.
Among the advantages of this system, we can mention:
- Reduction of risks and costs: by opening the innovation chain the organisation is sharing all project development with a third party. This allows all associated values and risks to be shared, without overburdening the company that owns the idea.
- Acceleration in the implementation of innovations: by involving external agents in project development, the tendency is for there to be an optimization of time. In these cases, the contracted third party shares its knowledge and technologies, making development processes faster and more efficient.
- Improvements to already implemented products and services: open innovation not only guarantees new products, but allows, with the acquisition of external knowledge, that products and/or services already implemented in the company are enhanced.
- Strengthening Branding: in this innovation model, the company opens its doors to the entire market. Obtaining partners contribute to publicising the business, proactively strengthening branding.
- Relevant Networking: collaboration brings together companies with the same profile and development objective as yours, in addition to integrating creative forces, talents and skills. It strengthens professional networking, creates relevant brand association within the market, and further spreads new ideas.
- Increased ROI: Return over Investment is an indicator that allows you to know how much money the company earns with each investment made. With the implementation of Open Innovation, the company tends to have a greater return on investment, as innovation is implemented quickly, cheaply, and safely promotes a chance of obtaining greater profits.
However, it is still important to remain aware of possible challenges, such as the possibility lack of clarity on objectives being pursued, lack of communication and coordination between the parties involved, selection of ideas, and intellectual property rights resulting from collaboration.
What is happening in the rest of the world?
Open Innovation is still growing. According to Economist Impact’s 2021 Open Innovation Barometer, OI’s current framework demonstrates profound progress across all sectors studied, with an average score of 62.9 (on a scale of 0 to 100, with 100 being fully open), in which large companies demonstrate greater adoption of OI Practices. As Open Innovation ecosystems advance, so does interest and implementation in the most diverse environments: also, according to this report, 95% of respondents stated that their companies practice OI, with 54% applying the practices in all or most of their projects, and 90% that have implemented key pillars of this method or plan to implement them.
In Europe, Sopra Steria’s Open Innovation Report 2023 shows a rapid uptake of OI, with almost 3 in 4 (72%) European companies conducting projects in collaboration with startups, based on around 1,648 companies and startups from 10 countries. The data also shows 89% of objectives were achieved in corporations that managed collaborations using a dedicated business unit.
The Panorama of Open Innovation in Companies in Brazil, a study released by Softex, also indicates that Open Innovation is present in 88% of Brazilian companies, considering companies of all sizes, markets, and regions of the country, having a variety of partners: 67% startups, but also including universities, companies, among other. The concept of Open Innovation is increasingly widespread in society, with the economic and competitive landscape demanding that companies implement increasingly agile and technological processes. In this way, Open Innovation process becomes a viable and good option due its opening of the innovation chain, optimisation of processes and improvement of ideas, orbiting companies, institutions, and other pillars of the market, such as universities, innovation hubs and government.
The concept of digital twins has emerged as a powerful tool across various industries in recent years, revolutionizing the way organizations design, operate, and manage complex systems.
From astronomy to smart cities, digital twins are reshaping the landscape of innovation, and driving efficiency, productivity, and sustainability.
Data-driven learning systems
Definition
A digital twin is a virtual replica or simulation of a physical asset, process, or system that enables its real-time monitoring, analysis, and optimization.
The object under study is equipped with various sensors linked to vital areas of its functionality. These sensors generate data on several aspects of the physical object’s performance. The data are then sent to a processing system and applied to the digital copy.
Once populated with the data, the digital copy can be used to run simulations, investigate performance issues and develop possible improvements, all with the aim of generating valuable information.
The 4 types of digital twin
Digital twins are divided into 4 levels, bottom-up, depending on the integration level of data and parameters:
- Level 1: Component Twin
- This represent the smallest elements of a system such as a specific part of the equipment or product.
- Level 2: Digital Product Twin
- Virtual representations of physical products or assets.
- Level 3: System Twin
- These represent entire systems or ecosystems, embracing multiple interconnected components, processes, and stakeholders.
- Level 4: Digital Process Twin
- Replicates the behaviour and dynamics of complex processes or systems, such as manufacturing processes, supply chains, or industrial operations.
Application: industrial uses of digital twins
Automotive/transportation: driving innovation with digital vehicle twins
Digital vehicle twins allow engineers to analyse how different factors such as aerodynamics, fuel efficiency, and safety features impact the overall performance. By simulating various driving conditions and scenarios, engineers can identify potential issues, refine designs, and improve the reliability and safety of vehicles.
The twins also enable predictive maintenance and condition monitoring of vehicles, enabling fleet operators to anticipate maintenance needs, minimize downtime, and optimize asset utilization.
Telecommunications: efficient networks and better customer experience
Telecommunication companies use digital network twins to create virtual replicas of their infrastructures, including towers, antennas, switches, and cables. These digital twins simulate network behaviour, traffic patterns, and performance metrics, enabling operators to identify bottlenecks, predict capacity requirements, and optimize resource allocation.
By integrating real-time data from network elements, sensors, and customer interactions, digital network twins provide operators with actionable insights into network health, enabling proactive maintenance, fault prediction, and service restoration.
Construction: building the future with BIM
In the construction industry, digital twins are known as Building Information Models (BIM). BIMs are a digital representation of a building or infrastructure project that mirror the geometry, spatial relationships, and other relevant data.
Digital twins of construction projects enable architects, engineers, and contractors to collaborate more effectively, visualize designs in 3D, and identify potential conflicts or errors before the start of construction. By simulating construction processes and sequencing activities, BIMs help to optimize project schedules, reduce costs, and improve project efficiency overall.
Medicine: personalized proactive patient care with digital health twins
Digital health twins are virtual representations of individual patients. They enable clinicians to tailor treatment plans and interventions to the patient’s unique medical history, genetic makeup, and lifestyle factors.
By analysing data from wearable devices, electronic health records (EHRs), and medical imaging, clinicians can identify trends, detect early warning signs, and intervene proactively to prevent adverse health outcomes.
Pharmaceutical companies can leverage digital twins to simulate drug interactions, predict drug efficacy, and identify patient subpopulations for targeted therapies, leading to more efficient drug discovery and development processes.
Smart cities: optimizing urban systems with citywide twins
In smart cities, digital twins are known as citywide twins. By modelling transportation networks, energy grids, water systems, and other critical infrastructure, citywide twins help to identify inefficiencies, anticipate future needs, and develop strategies for sustainable growth. They also support resilience to and preparedness for disasters by modelling the impact of natural catastrophes, pandemics, and other crises. In addition to which they also facilitate citizen engagement and participatory planning by providing interactive platforms for residents to explore urban data, provide feedback, and contribute to the development of their communities. By fostering transparency and collaboration, citywide twins empower citizens to play an active role in shaping the future of their cities.
Astronomy: exploring the cosmos with virtual observatories
Digital twins of telescopes allow astronomers to test different configurations, calibrate instruments, and optimize their performance before conducting actual observations. In addition, virtual observatories can integrate data from multiple telescopes and sensors, enabling astronomers to correlate observations and detect hidden patterns in the vastness of space.
The development of new technologies has changed our perceptions and how we grow businesses of late, bringing a range of new concepts and routines to our daily lives. Web 3.0 and metaverses, for example, are two emerging technologies that are expected to revolutionize the way we do business in the years to come, and continually scrutinized and evaluated at this point in time.
Web 3.0
Web 3.0, which may also be known as the semantic web, is a concept developed for the next generation of the world wide web, using artificial intelligence (IA) and learning algorithms as well as blockchain technologies to understand data in their sharing, and facilitate the search for information and its storage in a decentralized computer network, based on the context.
Blockchain is a method of storing information – i.e. a database – that is shared among a network of computers and duplicates and distributes transactions and information, making it difficult or impossible for the system to be manipulated and hacked.
Compared to the current internet network – referred to as Web 2.0 – a decentralized web would offer greater security and privacy, along with more data ownership, as it allows users to manage and control their personal information, rather than relying on the architecture of a central server and its relationship with the client, as is the case today.
Metaverse
“Metaverse” is a term referring to virtual worlds that allow online social interaction using digital avatars, embracing virtual reality (VR) or augmented reality (AR) technologies to create an immersive experience. Within the space created, aspects of the physical world are simulated and reinforced through resources such as social media and digital currencies, as well as avatars, events, online activity centres, etc., elements that vary from one platform to the next.
In the last two decades, the emergence and proliferation of games promoting popular metaverses, such as Minecraft and Second Life, have engendered attempts to create ever more platforms aiming to integrate virtual and physical spaces in metaverse interactions.
Technology and business
According to Citi, metaverse businesses are expected to contribute between $ 8 and $13 trillion to the global economy by 2030, with an estimated five billion users. But what is more important to start with is to consider the users likely to go for these new technologies, and what they are looking for.
In the most popular metaverses such as Roblox and Minecraft, people in general and generation Z (born between 1997 and 2010) in particular are increasingly spending their money on virtual items and accessories, many of them exclusive to the respective metaverse. Which indicates that, apart from creating virtual versions of existing physical products, there are also development potentials for unique virtual products and experiences.
Marketing can play a key role in this, too. In 2022, major brands like Disney and Nike announced strategies or projects that embraced metaverses as a new means of engaging with customers, of broadening the understanding and study of online consumer behaviour, and enabling even more personalized and precisely focused experiences tailored to the interests and needs of each target audience.
Web 3.0 could likewise enhance customer relationships. Trust-building between businesses and their customers is eased given the transparency ensured by the «immutability» of data stored in blockchain technologies, infusing the latter with greater confidence in the information’s authenticity. Better legal compliance is another benefit, with immutable transaction records that are transparent to all parties helping businesses meet governance requirements.
As Web 3.0 is designed to be decentralized, applications are unlikely to require expensive servers and data centres, and can be run on computer networks provided by end users, eliminating the need for third-party service providers. Another cost-saving benefit is the potentially easier supply chain monitoring, enabling possible issues to be identified with greater agility and better time management.
What is the upshot for us?
Web 3.0 and metaverses are highly networked in their focus on sharing content and experiences online, and both based on advanced technologies such as the AI employed in their development and blockchains, a concept undergoing constant evaluation as an integral element of Web 3.0, set to power metaverse services.
Although adjustments may be necessary, the future potential of these two technologies is huge and highly promising, offering countless opportunities for innovation in a new digital wave able to change the way we do business in all kinds of ways. Potential challenges do exist – such as the incorporation of Web 3.0 in the metaverse, potentially leading to a virtual world that is fully integrated with the internet, or the availability of resources that support these new tools – but they can be overcome with time, promising a new era of access and change.
What is the Digital Transformation?
The digital transformation is not just one thing or activity, but an entire process by which companies enhance the digital technology in their businesses, using it to change or create new processes, cultures, and customer experiences, optimising all the activities right from the start. The process can vary from one company to the next, depending on how the technology is applied and implemented.
Many ways lead to digital transformation and its changes, and every organisation’s journey will be unique. A company might add AI as a tool for optimising the customer experience or for developing new strategies to make its daily team routines more efficient. The organisation’s operations are rewired by the constant evolution and integration of technologies that improve its functions.
To be successful, the digital transformation calls for a variety of coordinated activities: it is a long-term effort with continuous adaptations and changes.
Defining Digital Transformation Strategies
- Transformation business strategy: The technological route you opt for now will decide your company’s success.
- Realigning business operations: What do your customers and employees need most, and how can digital processes help? The design of better processes can be based on these questions.
- Adoption of new practices for agility and experimentation: As customer expectations mount and the pace of change quickens, new ways of working need to be introduced. To be successful, the digital transformation needs to pursue a varied approach that pays heed to the availability of technologies and human adaptability.
- Flexible core technologies for sustainable change: By staying flexible, you can catalyse innovation across your enterprise and form ecosystem partnerships more easily to drive speed and scale. It is important not to get stuck with just one technology. Openness to new possibilities and improvements allows for fast and sustainable changes, while keeping the needs of your client or team in focus is key.
- People management: How can technologies enable better knowledge sharing and collaboration? What should the future of work look like? Technologies face workers with new challenges, but can also solve many of them. To make them work, the digital basis, digital operations and digital skills of the workforce all need to be supported by the management and a culture that welcomes new technologies and seeks the best ways of integrating them in everyday life.
Digitalisation vs. Digital Transformation
Even if the mention of digital transformation will automatically make you think of digitalisation, it is important to emphasise that the two are not the same. Digitalisation can be seen as an integral part of the digital transformation process and one of its ultimate pillars. But what is important even before this point is to first identify the requirements and possible improvements between teams and customers and their systems, and then set up a process for changing the culture and adapting routines to the new system installed.
Digitalisation is mostly about technologies – their application to change a business and automate business processes, step by step or rolled-out as a project – whereas the digital transformation is not, but can include digitalisation as an integral part in its continuing quest for new procedures while paying greater attention to people and their attitude to changes in the company culture.
What does the digital transformation mean for FI Group?
In FI Group, too, the digital transformation is brought about in the most diverse ways, all aimed at providing added value for clients and employees. The digital transformation here proceeds incrementally in a stream-aligned structure – a model of organisation and team interaction where squads with digitalisation strategies for services in various areas globally develop and manage digital tools for teams and clients.
Applying new ways of systematising documents and data is meanwhile another operative element of the digital transformation – the establishment of new organisational methods facilitates and speeds up the work and access to required information.
More locally, we also have our Scientific Department, established by FI Group France in 2019, which leads the research relating to artificial intelligence and NPCs, aiming to enable a regular scientific and technological supervision for proposing new approaches and supporting R&D Financing Consultants in their daily missions.
OpenAI, Chat GPT, and generative language models
2023 will go down as the breakthrough year for ChatGPT due to the intuitive capabilities and wide scope of applications of the tool.
But where did it all start?
Created in 2015, OpenAI has notable founders such as Elon Musk and Sam Altman with the aim of integrating artificial intelligence into society for the benefit of humanity. Looking back on the last seven months, you can definitely say their work has impacted society through their creation of ChatGPT.
In a nutshell, ChatGPT is an AI application that has been ‘trained’ to understand natural language and conversation. Pulling data from the internet and presenting its findings in easy to understand responses. Furthermore, it can be used as a translator, create content, summarise text and process / write code.
The R&D
Ironically, you can find out about the R&D behind ChatGPT by simply asking it. The tool identifies five components that make up its development:
- Training Data – Large amounts of text, sources that include books, articles, and websites – where it can capture grammar and context.
- Pre-Training – Learning to predict the next word in sentences and understand the patterns and relationships it sees from its training data.
- Fine-tuning – Final stages of learning translation, question answering, and conversation.
- Architecture and Algorithms – Transformer models help natural language processing tasks, for example, capture contextual relationships effectively.
- Iterative Development – The final stage of testing the previous four components, making fine adjustments to any imperfections.
However, it can be difficult to put all this development into perspective and understand the gravity of its intelligence. The English language is comprised of one million words. In comparison, ChatGPT is made up of ten billion words, including fifteen languages (incl. English, French, Russian, Chinese, Arabic and Urdu), and sixteen programming languages (incl. Python, Java, JavaScript, C++ and, HTML/CSS).
If you wanted to dive deeper into the development of the tool, tokenization is the breaking down of the sequence of text into smaller units, appropriately called tokens. These help ChatGPT’s natural language processing (NLP) for further development.
Applications
As previously mentioned, OpenAI reached their goal of impacting society through their work. The applications for ChatGPT are vast, content creation, consultancy, and customer support to name a few.
A popular term being used more and more within industries is, ‘ChatGPT won’t take people’s jobs, people that use it will’. Which to an extent is correct. If utilised correctly by competent professionals with in-depth knowledge of their profession, then ChatGPT can allow for streamlined workflows and increased productivity.
Despite having ten billion words, mistakes can still be made. Users who copy and paste its responses risk not only incorporating the errors the tool might have created but also limiting themselves by hindering personal development in their respective careers.
Introducing MarIA
FI Group has made the decision to move away from ChatGPT. At a glance this decision might undermine what was said previously about streamlining workflows, however, we have opted to use a different tool. We are launching MarIA which uses AzureGPT functions. Similar to ChatGPT, but can ensure that conversations and data shared with it remain in the Azure environment which provides an additional level of security.
On the topic of ChatGPT, FI Group France Scientific Director Charlie Grosman said:
‘while it generates useful and relevant information, in a short period of time, it is not a technology that employees should trust at an exact level».
What does MarIA mean for our clients?
FI Group requires a lot of sensitive information from our clients such as confidential R&D project details and employee salary, if this information is shared with ChatGPT it is then stored in OpenAI’s database and outside of our control. MarIA ensures that any private information is kept safe in our own database and cannot be accessed by anyone outside of FI Group.
Moreover, MarIA will also limit how much FI Group employees can use its functions. Ensuring that work is being done by real people and aided by the tool, when necessary, rather than the other way round. Meaning, clients can be assured they are getting genuine expert client opinions.
What is Articifial Intelligence (AI) ?
Articifial Intelligence is a technology that belongs to the field of computer science and aims to create systems and algorithms that run in a dynamic environment, based on the collection and processing of data. These computer programs must be able to simulate human intelligence. The main objective of AI is to create intelligent machines that can help solve complex problems in many fields.
There are several categories of Articifial Intelligence (AI), which can be classified according to their capability and level of sophistication. Here are some of the most common categories of Artificial Intelligence :
- Weak Articifial Intelligence : This category of AI can perform specific and limited tasks. It is often used for applications such as speech recognition or image classification. While it is very effective at specific tasks, it can’t replicate the versatility of human intelligence.
- Strong Articifial Intelligence : This category of AI is designed to replicate human intelligence in its entirety. It can think autonomously, solve complex problems, and perform a wide variety of tasks without being explicitly programmed for each one. However, strong AI does not yet exist in its entire form and scientists continue to work on ways to develop it.
- Super Articifial Intelligence : This category is a hypothetical version of AI that would be capable of surpassing human intellectual abilities in all areas. This form of AI does not yet exist, but some AI experts predict that it could be developed in the future.
To get as close as possible to human behaviour, Articifial Intelligence needs a lot of data, as well as a processing and learning capacity. To achieve this, three components are needed:
- Computer systems,
- Data with management systems (they can be collected from databases, files, etc.),
- Algorithms. Once the data has been processed, a machine learning model can be trained using algorithms. This model is then trained to learn to perform a specific task from the data autonomously.
To enable computers to learn from data, Articifial Intelligence relies on Machine Learning models (a method that aims to teach machines to learn from data and improve with experience). There are 3 learning methods used:
- Supervised: which uses defined data to learn to identify patterns and make predictions,
- Unsupervised: which learns from undefined data. It uses techniques such as clustering or dimension reduction to identify patterns and relationships in the data,
- Semi-supervised: uses both defined and undefined data.
It is important to note that AI is a constantly evolving field of research, and that definitions and distinctions between different types of Artificial Intelligence may change.
What is Articifial Intelligence used for?
The main goal of AI is to create intelligent machines that can help solve complex problems in many fields, such as medicine, engineering, finance, security, social sciences, gaming, etc. Articifial Intelligence is seen as a key technology for the future and has the potential to transform the way we live and work.
These examples are just a small portion of the application areas for AI, and new uses are regularly discovered as the technology continues to advance. AI can therefore be used to improve efficiency, accuracy, safety, and quality in many different areas.
The example of ChatGPT
One of the most popular supervised AI at the moment is Chat GPT (Chat Generative Pre-trained Transformer). This conversational tool aims to help its users solve problems, answer questions, and provide information in various domains. It therefore generates text from input data (questions, queries, etc.). It is based on Natural Language Processing technology (NLP) and uses unsupervised learning. It has been trained on a very large corpus of text to learn how to generate consistent and relevant answers based on user queries. This is possible because it has access to huge amounts of text, from various sources.
FI Group Scientific Department
As a pure player in the R&D ecosystem, FI Group France has created a Scientific Department back in 2019. They lead research in Artificial Intelligence and NLP mostly. This department is composed of seven Researchers (including two Industrial PhD CIFRE). One PhD student is conducting a thesis on data extraction and the construction of algorithms to evolve their grouping by theme and subject. The second PhD student is doing a thesis on unsupervised learning on data flows. She is developing methods capable of clustering data continuously.
The objective of this department is to allow the realization of a regular scientific and technological watch to propose new approaches, and thus to support R&D Financing Consultants in their daily missions.
These projects are possible thanks to the development and experimentation of techniques in Machine Learning and Automatic Language Processing. These processes facilitate the search for information in a large volume of data. A third research topic concerns the acquisition of new knowledge and the involvement of collaborators, via Gamification processes and serious games.
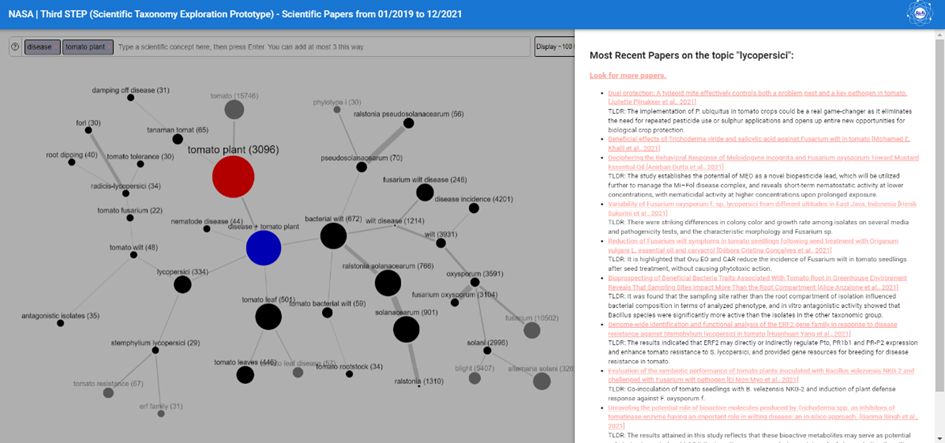
The NASA project
One of the projects supported by FI Group is called NASA. This AI makes it possible to search for scientific articles based on various concepts.
For each query, the articles published between 2019 and 2021 (about 13 million) are used to represent this knowledge in the form of a graph of concepts. It is then possible to display 10 scientific articles published for each concept.
The first prototype of NASA «First STEP» (Scientific Taxonomy Exploration Prototype) was launched in March 2022. The second and the third were respectively put online in September 2022 and February 2023. This «Third STEP» proposes improvements in performance, quality and user experience.
Why does digital transformation matter?
Case studies have argued that 50% of employees could be replaced by machines because of the big technological advancements in AI in the era of Digital Transformation, however, we see this as a complement instead as a negative human replacement.
We see computer software’s and AI as an addition to our activities, working alongside people who are part of the chain of vision. People can improvise, be reactive and think critically, showcasing the advantage of people in unexpected situations. There is a clear link between the collaborative work that can be done by AI and people, rather than a separation.
Knowing how to be an efficient and productive team is always the main aim of any successful partnership. As discussed, both people and AI have different strengths and weaknesses. By delegating tasks based on these strengths and weaknesses the digital transformation and partnership between people and AI can become more efficient and impactful.
What role does consultancy play in digital transformation?
It is becoming harder and harder to talk about Consultancy without mentioning digitisation. The digitisation of consultant tasks can be eased by Robotic Process Automation (RPA) software’s. These systems are designed to emulate human’s actions when interacting with digital systems, such as recognising and extracting relevant data.
This automation undoubtedly contributes to the streamlining of the consulting process. It can gather information immediately, transfer documents instantly, create news queries in a few minutes, solve the incidences quickly and in the stages of verifying or making changes to procedures.
So, the digital transformation allows for flexibility within automation systems, which develops ease and efficiently, making the consultants project writing time shorter. This is also a benefit for the client as it allows for quicker turn around time on R&D reports.
Focusing on the improvement of the value add of our services has always been one of our greatest priorities. Innovation and technology are core pillars of our business, we are always looking for ways to improve our internal procedures through digital advancements that are being made, to provide the best and most efficient results for our clients.
The FI Group solution
- How can FI Group help our clients in this era of digital transformation?
We offer a free audit to highlight and show our clients areas in their R&D process that can be improved by our team and service.
To improve this process, we have created an application that have improved the line of communication between FI Group and clients, and allows 24h access to updated claim information, improving our traditional services through new digital tools.
Introducing FI Connect. A new digital space that integrates several applications on a single platform. Benefiting our customers by providing greater transparency and showcasing the digital transformation that FI Group is currently undergoing and that will drive productivity for clients and consultants alike.
Welcome to FI Connect
Find out if the service is available in your country to book a demo:











